CSRP2 transcript levels after consolidation therapy increase prognostic prediction ability in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9034Keywords:
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), relapse, measurable residual disease (MRD), cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 (CSRP2), multi-parameter flow cytometry (MPFC)Abstract
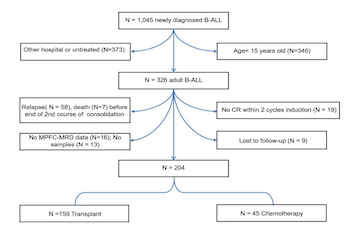
Quantification of measurable residual disease (MRD) correlates with the risk of leukemia recurrence in adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, it remains unknown whether collecting data on cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 (CSRP2) transcript levels, after completing the second course of consolidation, improves prognosis prediction accuracy. A total of 204 subjects with B-cell ALL were tested for CSPR2 transcripts after completing the second course of consolidation using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and divided into high (N = 32) and low (N = 172) CSRP2 expression cohorts. In multivariable analyses, subjects with high expression of CSRP2 had a higher 5-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.57, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.38-4.76; P = 0.003), lower 5-year relapse-free survival (RFS) (HR = 3.22, 95% CI 1.75-5.93; P < 0.001), and overall survival (OS) (HR = 4.59, 95% CI 2.64-7.99; P < 0.001) in the whole cohort, as well as in the multi-parameter flow cytometry (MPFC) MRD-negative cohort (for CIR, HR = 2.70, 95% CI 1.19-6.12; for RFS, HR = 4.37, 95% CI 1.94-9.85; for OS, HR = 4.90, 95% CI 2.43-9.90; all P < 0.05). Prognostic analysis showed that allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) could significantly improve the prognosis of patients with high CSRP2 expression (allo-HSCT vs chemotherapy: 5-year CIR, 52% vs 91%; RFS, 41% vs 9%; OS, 38% vs 20%; all P < 0.05). Our data indicate that incorporating data from CSPR2 transcript levels to the MRD-testing at the end of the second course of consolidation therapy enhances prognosis prediction accuracy in adults with B-cell ALL.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Lei-Ming Cao, Ya-Lan Zhou, Robert Peter Gale, Ya-Zhen Qin, Li-Xin Wu, Ming-Yue Zhao, Xiao-Su Zhao, Yu-Hong Chen, Yu Wang, Hao Jiang, Qian Jiang, Ying-Jun Chang, Yan-Rong Liu, Lan-Ping Xu, Xiao-Hui Zhang, Xiao-Jun Huang, Guo-Rui Ruan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-05-07
Published 2023-11-03









