Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on management of surgically treated laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9481Keywords:
COVID-19 pandemic, laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), treatment modality, adjuvant therapyAbstract
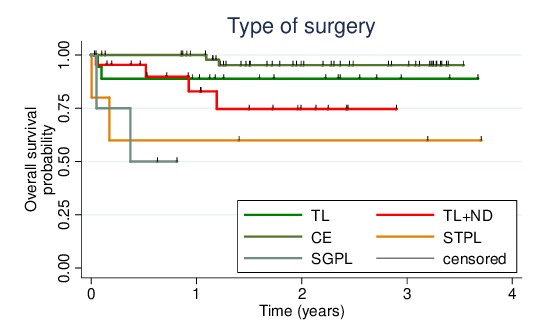
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has significantly impacted the treatment of cancer patients, particularly in terms of treatment choices. This study aimed to assess the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the management of surgically treated laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) patients, focusing specifically on changes in treatment modalities. We retrospectively analyzed the data from 102 patients who underwent surgical treatment for LSCC between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2021, at our tertiary medical center. Patient demographics, histological characteristics, and treatment modalities were extracted from electronic medical records and compared between two time periods: pre-COVID-19 and during COVID-19, marked by the introduction of the hospital entry triage. Of the total patients, 53 (52%) were in the pre-COVID-19 group, and 49 (48%) were in the COVID-19 group. No significant differences in patient characteristics at the initial work-up were observed between the two groups. However, a significant shift in treatment modalities was noted. Fewer patients received postoperative adjuvant therapy in the COVID-19 group (70.5%) compared to the pre-COVID-19 group (95.5%). Importantly, this change did not significantly impact the one-year overall survival (OS) rates. The reduction in the use of postoperative adjuvant therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic may be attributed to efforts to minimize hospital visits due to the risk of COVID-19 infection. Further research is warranted to validate these findings and to investigate the potential effects of such changes in treatment modalities on the long-term survival.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Alexander Lein, David T. Liu, Markus Haas, Almir Salkic, Azra Ibrisevic, Sabrina Uscuplic, Alen Harcinovic, Taria Brkic, Thomas Thurner, Faris F. Brkic

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-08-24
Published 2024-01-03









