A novel machine learning-derived four-gene signature predicts STEMI and post-STEMI heart failure
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9629Keywords:
ST-elevation myocardial infarction, heart failure, monocyte, machine learning, prediction modelAbstract
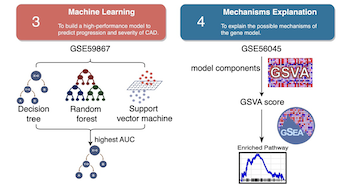
High mortality and morbidity rates associated with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and post-STEMI heart failure (HF) necessitate proper risk stratification for coronary artery disease (CAD). A prediction model that combines specificity and convenience is highly required. This study aimed to design a monocyte-based gene assay for predicting STEMI and post-STEMI HF. A total of 1,956 monocyte expression profiles and corresponding clinical data were integrated from multiple sources. Meta-results were obtained through the weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and differential analysis to identify characteristic genes for STEMI. Machine learning models based on the decision tree (DT), support vector machine (SVM), and random forest (RF) algorithms were trained and validated. Five genes overlapped and were subjected to the model proposal. The discriminative performance of the DT model outperformed the other two methods. The established four-gene panel (HLA-J, CFP, STX11, and NFYC) could discriminate STEMI and HF with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.86 or above. In the gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), several cardiac pathogenesis pathways and cardiovascular disorder signatures showed statistically significant, concordant differences between subjects with high and low expression levels of the four-gene panel, affirming the validity of the established model. In conclusion, we have developed and validated a model that offers the hope for accurately predicting the risk of STEMI and HF, leading to optimal risk stratification and personalized management of CAD, thereby improving individual outcomes.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jialu Yao, Yujia Zhou, Zhichao Yao, Ye Meng, Wangjianfei Yu, Xinyu Yang, Dayong Zhou, Xiaoqin Yang, Yafeng Zhou

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-09-05
Published 2024-03-11









