Plasma miR-19b, miR-34a, and miR-146a expression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cataract: A pilot study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9933Keywords:
Cataract, diabetes mellitus (DM), diabetic retinopathy (DR), microRNAs (miRNAs), biomarker, qRT-PCRAbstract
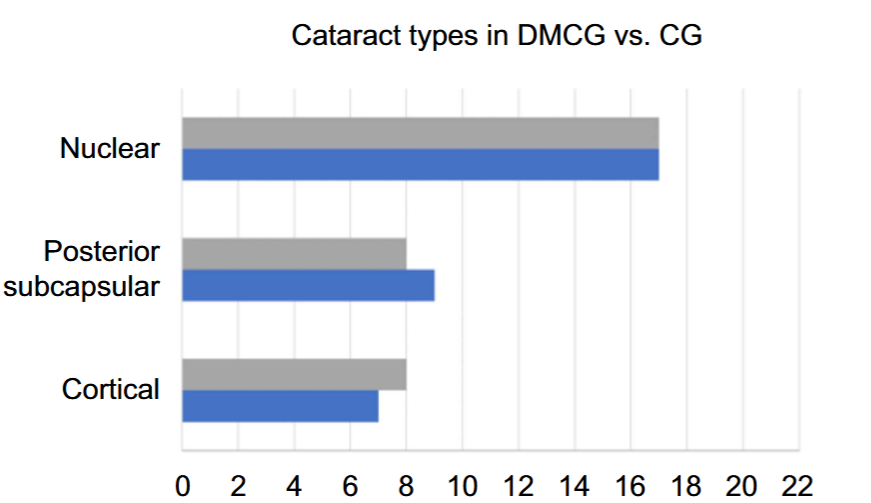
Cataract is among the most common ocular complications in diabetes mellitus (DM). While microRNA (miRNA) dysregulations in DM have been previously reported, consensus is still lacking concerning miRNA expression in cataract. Furthermore, the miRNA profile in diabetic cataract patients remains largely unexplored, and data on plasma expression levels are limited. Our study aimed to assess the plasma levels of three distinct miRNA species (hsa-miR-19b, hsa-miR-34a, and hsa-miR-146a) implicated in the development of cataract and/or DM.We investigated the circulating miRNA expression in DM patients diagnosed with cataract, compared to a non-DM cataract group. We employed qRT-PCR for relative quantification experiments and subsequently conducted a correlation analysis between miRNA expression levels and clinical characteristics. Our findings reveal that hsa-miR-34a and hsa-miR-146a are differentially expressed in the two cohorts. However, no significant correlation was observed between the clinical variables and miRNA levels. In summary, our results suggest a potential role for hsa-miR-34a and hsa-miR-146a in the biology of diabetic cataract.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Adina Iuliana Milcu, Flavia Medana Anghel, Mirabela Romanescu, Aimee Rodica Chis, Andrei Anghel, Ovidiu Boruga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-11-19
Published 2024-05-02









