Electrophysiological Effects of Bosentan in Rats with Induced Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2013.2358Keywords:
Bosentan, cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, electroencephalography, ratAbstract
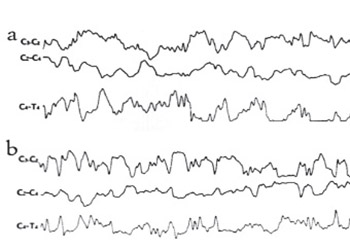
We examined the effect of bosentan, an ETA and ETB receptor antagonist, on EEG, an indicator of neuronal activity, in rats with experimentally induced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. The rats were divided into three groups with seven rats in each group. Before the procedures, the EEGs of all rats were recorded for ten minutes. 30 mg/kg bosentan in 2 cc physiological serum was administered to the first group, and the second and third groups were injected with 2 cc physiological serum intraperitoneally. After the administration, the right and the left common carotid arteries of the animals in Groups 1 and 2 were clipped for 10 minutes using aneurysm clippings. The rats in the third group received only a subcutaneous incision. Ten minutes after the clips were removed in the first and second groups and after the incision in the third group, EEG recordings were repeated for 10 minutes. All the rats were decapitated and MDA values in the brain tissue were measured for evaluation of the efficiency of induced cerebral ischemia. Induced cerebral ischemia was performed effectively because the MDA levels in Groups 1 and 2 were elevated, compared to the levels in Group 3 (p<0.05). After the application of the Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Technique, the EEG showed minimal slowing in the rats in Group 1, and generalized diffuse slowing in the rats in Group 2 compared to pre-ischemic findings. Bosentan may reduce the damage induced by ischemia on neuronal electrophysiology, likely through its vasodilation effect on cerebral vessels.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-08-13
Published 2013-08-20









