Clinical diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with microflow imaging in benign and malignant renal tumors: A retrospective cohort study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10236Keywords:
Renal tumor, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), microflow imaging (MFI), color doppler flow imaging (CDFI), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curveAbstract
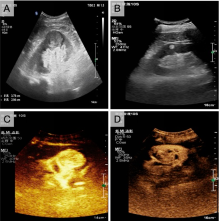
This study aims to evaluate the clinical diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with microflow imaging (CEUS-MFI) in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant renal tumors. All patients underwent CEUS, MFI, color doppler flow imaging (CDFI), and CEUS-MFI. The efficacies of these different diagnostic modalities in diagnosing benign and malignant renal tumors were evaluated by Kappa consistency test and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, with pathological findings serving as the gold standard. CDFI, MFI and CEUS-MFI all demonstrated higher blood flow in malignant tumors compared with benign tumors. Compared with benign tumors, CDFI detected a higher rate of punctate and linear Adler grade 2 and 3 blood flows in malignant tumors, as well as peripheral semicircular or annular blood flow. MFI identified a high rate of peripheral circumferential blood flow and irregular vascular morphology in malignant tumors, with most exhibiting Adler grade 3 blood flow. In addition, CEUS-MFI showed more dendritic or irregular Adler grade 2 or 3 blood flows in malignant renal tumors than MFI alone. Further analysis showed that CEUS-MFI had the highest consistency with pathological diagnosis (Kappa = 0.808). The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve (AUC) for CEUS-MFI in differentiating between benign and malignant lesions was 0.898, significantly outperforming other single diagnostic methods. With its capability to display microvascular information and assess overall pathological characteristics, MFI can accurately predict the nature of renal tumors and assist in surgical planning.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Xiufeng Kuang, Huiyang Wang, Weilu Chai, Huafang Yuan, Ting He , Mengya Shi , Tianan Jiang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









