Development and validation of a preliminary multivariable diagnostic model for identifying unusual infections in hospitalized patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10447Keywords:
Atypical infections, diagnostic delay, diagnostic model, multivariable model, rare infectionsAbstract
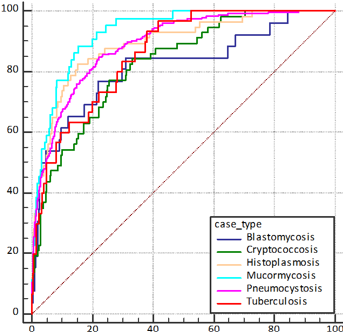
Diagnostic delay leads to poor outcomes in infections, and it occurs more often when the causative agent is unusual. Delays are attributable to failing to consider such diagnoses in a timely fashion. Using routinely collected electronic health record (EHR) data, we built a preliminary multivariable diagnostic model for early identification of unusual fungal infections and tuberculosis in hospitalized patients. We conducted a two-gate case-control study. Cases encompassed adult patients admitted to 19 Mayo Clinic enterprise hospitals between January 2010 and March 2023 diagnosed with blastomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, mucormycosis, pneumocystosis, or tuberculosis. Control groups were drawn from all admitted patients (random controls) and those with community-acquired infections (ID-controls). Development and validation datasets were created using randomization for dividing cases and controls (7:3), with a secondary validation using ID-controls. A logistic regression model was constructed using baseline and laboratory variables, with the unusual infections of interest outcome. The derivation dataset comprised 1043 cases and 7000 random controls, while the 451 cases were compared to 3000 random controls and 1990 ID-controls for validation. Within the derivation dataset, the model achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.87-0.89) with a good calibration accuracy (Hosmer-Lemeshow P = 0.623). Comparable performance was observed in the primary (AUC = 0.88; 95% CI: 0.86-0.9) and secondary validation datasets (AUC = 0.84; 95% CI: 0.82-0.86). In this multicenter study, an EHR-based preliminary diagnostic model accurately identified five unusual fungal infections and tuberculosis in hospitalized patients. With further validation, this model could help decrease time to diagnosis.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Data Availability Statement
The individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article, after de-identification, and the study protocol are available to researchers who provide a methodologically sound proposal from the corresponding author at any time.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Aysun Tekin, Mohammad Joghataee, Lucrezia Rovati, Hong Truong, Claudia Castillo-Zambrano, Kushagra Kushagra, Nasrin Nikravangolsefid, Mahmut Ozkan, Ashish Gupta, Vitaly Herasevich, Juan Domecq, John O’Horo, Ognjen Gajic

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









