Fiber-type composition and 3D capillary analysis of the human splenius capitis muscle
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10787Keywords:
skeletal muscle, splenius capitis muscle, vastus lateralis muscle, capillary network, myosin heavy chain isoforms, MyHC, 3D image analysis, humanAbstract
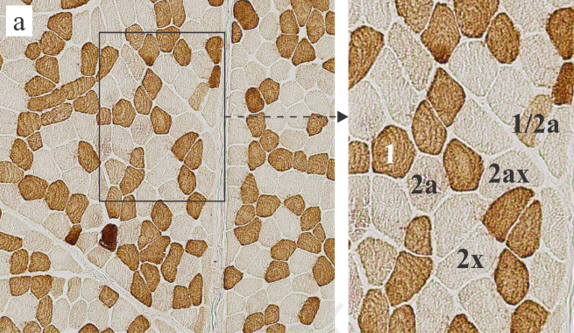
Despite the significance of neck muscles in musculoskeletal disorders, their microscopic anatomy remains poorly characterized. This study examined the splenius capitis muscle, focusing on its fiber-type composition, fiber size, and capillary network characteristics. For comparison and validation, the vastus lateralis muscle was also analyzed. Muscle samples from 13 young male subjects (mean age ± SD: 35.7 ± 8.6 years) were collected within 24-h post-mortem during autopsy. Myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoform expression was characterized immunohistochemically in 10 μm sections, while the capillary network architecture was assessed in 100 μm sections. Immunofluorescence staining, confocal microscopy, and 3D image analysis were employed to quantify capillary tortuosity, anisotropy, branch density (Br dens), and the length of capillaries per muscle volume (LV), per muscle fiber length (LL), per fiber surface area (LS), and per fiber volume (LVf). Compared to the vastus lateralis muscle, the splenius capitis muscle had a higher percentage of type 1 fibers (51.2% vs 39.7%), fewer type 2a fibers (16.2% vs 31.4%), and smaller fiber diameters (35.5–40.9 μm vs 47–56.1 μm). It also displayed lower Br dens (P = 0.0069), higher anisotropy (P = 0.0004), and lower LL (P < 0.0001) but higher LVf (P = 0.0486). In the splenius capitis muscle, body mass index (BMI) negatively correlated with LV (P = 0.0155), LS (P = 0.0091), LVf (P = 0.0137), and anisotropy (P = 0.0425), and positively correlated with tortuosity (P = 0.0473), indicating a reduction in the capillary network. In the vastus lateralis muscle, only LV (P = 0.0161) decreased with high BMI. This study characterized the fiber-type composition, fiber size, and 3D capillary network of the splenius capitis muscle, establishing a baseline for investigations into pathological muscle alterations.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nataša Pollak, Chiedozie Kenneth Ugwoke, Nejc Umek, Armin Alibegović, Jiří Janáček, Barbora Radochová, Erika Cvetko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









