Red cell distribution width to albumin ratio and mortality in acute pulmonary thromboembolism
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10791Keywords:
Pulmonary embolism, red cell distribution width to albumin ratio, RAR, red cell distribution width, RDW, prognosis, mortalityAbstract
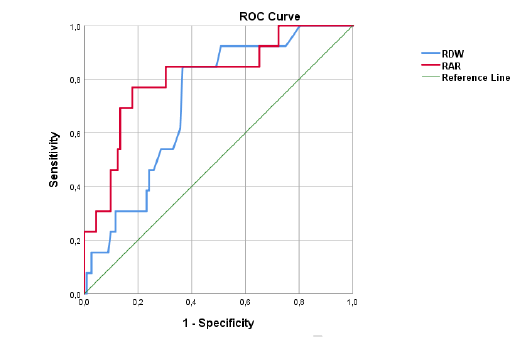
The red cell distribution width (RDW)/albumin ratio (RAR) is an inflammation-based prognostic biomarker. To date, its prognostic value in patients with pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) has been investigated in only one study. This study aimed to assess the effect of RAR on mortality in patients with PTE. Patients admitted for PTE between 2017 and 2023 were retrospectively reviewed. The data collected included demographic information, comorbidities, clinical findings, RDW, albumin, troponin, D-dimer levels, and in-hospital and 30-day mortality outcomes. RAR was calculated by dividing the RDW by albumin. A total of 190 patients were included in the study, of whom 83 (43.7%) were male. The mean age was 63 years (range: 23–89), and the mean RAR was 4.48% ± 1.68% /g/dL. A positive correlation was observed between RAR and both age and troponin level, whereas inverse correlations were noted with systolic blood pressure (sBP), diastolic blood pressure (dBP), and oxygen saturation (SpO2). Using a cutoff value of 5.294 determined by ROC analysis, patients with RAR ≥ 5.294 had a significantly shorter mean survival time than those with RAR value < 5.294 (16.310 months vs 35.163 months; log-rank test, P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified malignancy (hazard ratio [HR], 4.213; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.103–16.090; P = 0.035) and RAR (HR: 1.295, 95% CI: 1.035–1.621, P = 0.024) as independent predictors of survival. In conclusion, an RAR value ≥ 5.294 was associated with significantly shorter survival, underscoring its potential utility as a prognostic marker in clinical practice for non-massive PTE.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Berrin Zinnet Eraslan, Sumeyye Kodalak Cengiz, Ozlem Saniye İçmeli, Seda Beyhan Sagmen, Sevda Şener Cömert

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









