Regulatory role and molecular mechanism of METTL14 in vascular endothelial cell injury in preeclampsia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10963Keywords:
Preeclampsia, vascular endothelial cell injury, METTL14, miR-34a-5p, forkhead box protein 1, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modificationAbstract
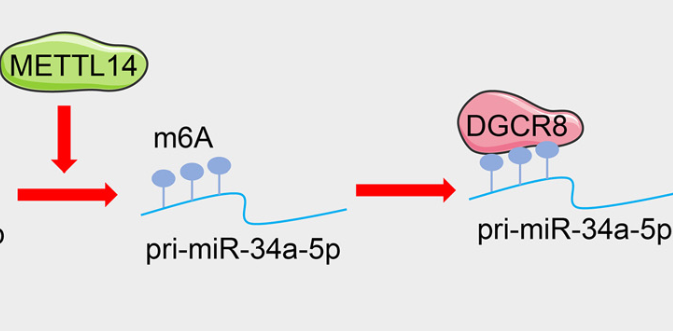
Preeclampsia (PE) is a pregnancy-related disease characterized by vascular endothelial cell injury. This study aimed to investigate the role of methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) in vascular endothelial cell injury in PE. A PE cell model was established by treating human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in vitro. METTL14 and forkhead box protein 1 (FOXP1) were silenced, and miR-34a-5p was overexpressed in HUVECs to evaluate their effects. HUVEC viability, apoptosis, and levels of intercellular adhesion molecule 1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and endothelin-1 were measured. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification of pri-miR-34a-5p was quantified. The interactions between miR-34a-5p, DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8, and m6A enrichment in miR-34a-5p were analyzed. The relationship between miR-34a-5p and FOXP1 was also verified. The results showed the expressions of METTL14, FOXP1, and miR-34a-5p. METTL14 expression was elevated in the TNF-α-induced HUVEC injury model. Silencing METTL14 improved HUVEC viability, inhibited apoptosis, and reduced endothelial inflammation. METTL14 promoted miR-34a-5p expression through m6A modification. Overexpression of miR-34a-5p or silencing FOXP1 reversed the protective effects of METTL14 silencing on cell injury in the PE model. In conclusion, METTL14 mediated m6A modification to promote miR-34a-5p expression, leading to FOXP1 inhibition, which aggravated endothelial cell damage in the PE cell model.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Huafang Wei, Lin Liang, Chengwen Song, Ming Tong, Xiang Xu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









