The gut microbiota modulates airway inflammation in allergic asthma through the gut-lung axis related immune modulation: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11280Keywords:
Asthma, gut-lung axis, gut microbiota, airway inflammationAbstract
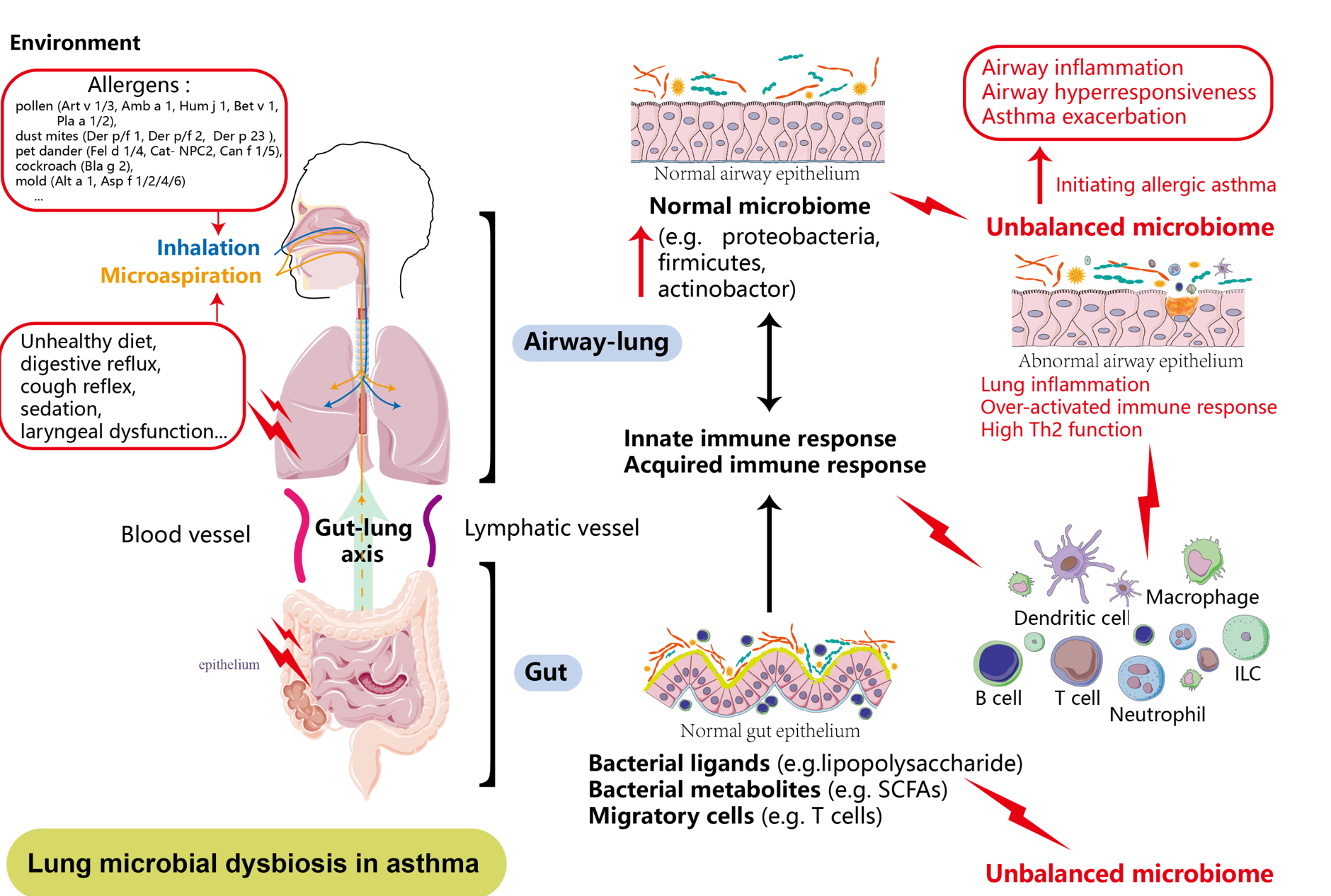
The human gut microbiota is a vast and complex microbial community. According to statistics, the number of bacteria residing in the human intestinal tract is approximately ten times that of total human cells, with over 1000 different species. The interaction between the gut microbiota and various organ tissues plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of local and systemic diseases, exerting a significant influence on disease progression. The relationship between the gut microbiota and intestinal diseases, along with its connection to the pulmonary immune environment and the development of lung diseases, is commonly referred to as the “gut–lung axis.” The incidence of bronchial asthma is rising globally. With ongoing research on gut microbiota, it is widely believed that intestinal microorganisms and their metabolic products directly or indirectly participate in the occurrence and development of asthma. Based on the gut–lung axis, this review examines recent research suggesting that the intestinal microbiota can influence the occurrence and progression of allergic asthma through the modulation of cytokine immune balance and mucosal integrity. Though the precise immune pathways or microbial species influencing asthma through the gut–lung axis are still under exploration, summarizing the immune modulation through the gut–lung axis in allergic asthma may provide insights for the clinical management of the condition.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Meng Zhang, Ziwen Qin, Chuanjun Huang, Bin Liang, Xiuqing Zhang, Weitao Sun

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









