Huangqi Decoction reduces liver fibrosis in rats by modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and promoting autophagy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11063Keywords:
Liver fibrosis, autophagy, Huangqi Decoction, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, apoptosisAbstract
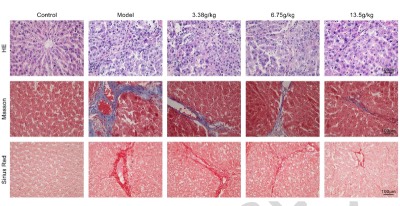
Liver fibrosis is a chronic condition caused by various factors, and currently, there are no widely effective treatments. Autophagy plays a crucial role in maintaining liver energy homeostasis, and its disruption can contribute to the development of liver fibrosis. This study investigates the effects and molecular mechanisms of Huangqi Decoction, a traditional Chinese medicine, on autophagy and apoptosis in fibrotic liver tissue. Tissue staining indicated that Huangqi Decoction mitigated CCL4-induced liver injury and apoptosis in rats. Western blot analysis of liver fibrosis markers revealed that Huangqi Decoction significantly reduced the expression levels of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), type I collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Additionally, serum markers of liver fibrosis and biochemical indicators of hepatocyte injury showed that Huangqi Decoction effectively lowered serum levels of hyaluronic acid (HA), lymph node (LN), type I collagen, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Furthermore, Western blot analysis confirmed that Huangqi Decoction alleviated hepatocyte injury by promoting autophagy and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. In conclusion, Huangqi Decoction enhances autophagy and inhibits apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in rats with liver fibrosis.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yingyin Mai, Tianlu Hou, Jiewen Shi, Yang Cheng

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









