Mitochondrial dysfunction in myasthenia gravis: Exploring directions for future immunotherapy? A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11197Keywords:
myasthenia gravis, mitochondria, immunity, metabolism, pharmacological effectsAbstract
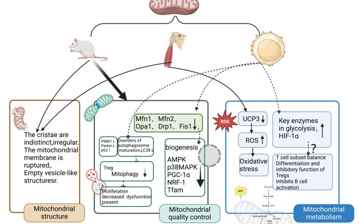
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an acquired autoimmune disease characterized by impaired transmission at the neuromuscular junction, primarily manifesting as fluctuating muscle weakness, fatigability, and partial paralysis. Due to its long disease course, treatment resistance, and frequent relapses, it places a significant burden on patients and their families. In recent years, advances in molecular biology have provided growing evidence that mitochondrial dysfunction impairs muscle function and affects immune cell proliferation and differentiation in patients. Mitochondria, as the cell's energy source, play a critical role in various pathological processes in MG, including oxidative stress, dynamic abnormalities, mitophagy, and mitochondrial metabolism. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of MG has garnered increasing attention. This manuscript primarily explores mitochondrial function and abnormal morphological changes in MG, as well as mitochondrial quality control, metabolic reprogramming, and their potential mechanisms in the pathological changes of the disease. It also reviews the current status of drug therapies aimed at improving mitochondrial function. The goal is to provide novel perspectives and strategies for future mitochondrial-targeted therapies in MG.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jianan Chen, Jing Lu, ZhiGuo Lv, Baitong Wang, Shanshan Zhang, Peng Xu, Jian Wang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









