The diagnostic accuracy of exosomes for glioma: A meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11268Keywords:
Biomarkers, diagnosis, exosomes, meta, gliomaAbstract
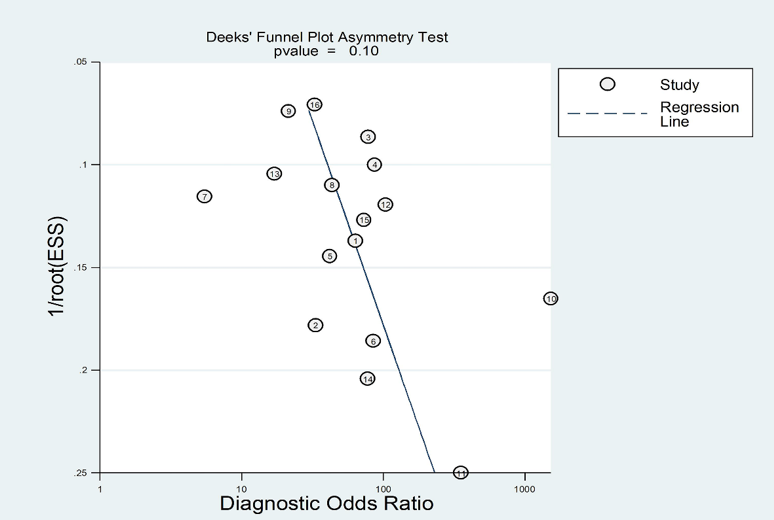
Glioma is one of the most prevalent primary intracranial tumors, and biomarker testing offers a non-invasive modality with high diagnostic efficiency. The aim of this meta-analysis is to evaluate the diagnostic effectiveness of exosomes as biomarkers for glioma. We included 16 studies on exosomes as biomarkers for gliomas. The pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the curve (AUC) for 25 biomarkers across these 16 studies were as follows: 82% (95% CI: 0.77-0.86), 91% (95% CI: 0.86-0.94), 9.10 (95% CI: 5.64-14.68), 0.20 (95% CI: 0.16-0.25), 45.94 (95% CI: 25.40-83.09), and 0.92 (95% CI: 0.89-0.94), respectively. Meta-regression indicated that biomarker analysis, biomarker type, and sample size may be sources of heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis suggested that ultracentrifugation (UC) was a better method for extracting exosomes. miRNA and other RNA groups (sncRNA, lncRNA, circRNA) provided higher SEN (0.88 vs. 0.84 vs. 0.78) compared to proteins. This study demonstrates the superior diagnostic efficacy of exosomes as biomarkers for gliomas, with high accuracy in diagnosing gliomas.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 XiangMin Zhang, YanDi Tan, XiaoYa He, Jie Huang, XiaoYing Ni, Qian Hu, JinHua Cai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









