Identification and validation of TUBB, CLTA, and FBXL5 as potential diagnostic markers of postmenopausal osteoporosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12019Keywords:
m6A, postmenopausal osteoporosis, PMOP, m6A methylation, diagnostic biomarkers, unsupervised clusteringAbstract
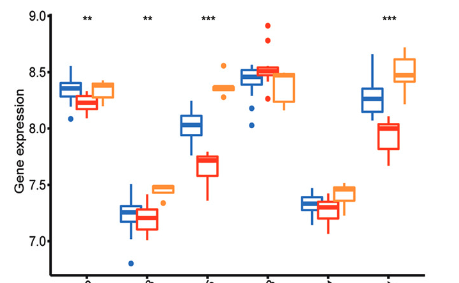
Postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) is recognized as the most prevalent bone disease worldwide. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most common RNA modifications influencing the progression of various disorders; however, its specific role in PMOP remains unexplored. This study aims to investigate the expression profiles of m6A-related genes and their impact on the prognosis of PMOP patients. We utilized the GSE56815 expression analysis dataset obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and extracted m6A-related genes for further examination. Our analysis revealed that m6A-related genes exhibited differential expression between PMOP patients and healthy controls. We employed consensus clustering to identify subgroups within the PMOP cohort and conducted immunological analyses on these clusters. Additionally, we intersected the clusters to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and analyzed potential diagnostic markers for PMOP using support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE), LASSO, and random forest (RF) algorithms, which were subsequently validated in the GSE56116 dataset. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to assess the diagnostic significance of these markers. Furthermore, quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed to validate the expression of the identified genes. In the GSE56815 dataset, we identified three subtypes associated with m6A modifications, leading to the identification of 302 shared DEGs among these subtypes. Gene ontology (GO) analysis indicated that the DEGs were predominantly enriched in nuclear specks, the nuclear envelope, and nucleocytoplasmic transport processes. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis further revealed that DEGs were primarily associated with endocytosis and nucleocytoplasmic transport pathways. Through the application of SVM, LASSO, and RF algorithms, we identified three potential diagnostic markers: TUBB, CLTA, and FBXL5, which demonstrated promising diagnostic capabilities when tested against an independent dataset. qPCR validation confirmed significant expression differences of these genes between the control and PMOP groups. The genetic markers identified in this study hold potential for accurately predicting the risk of PMOP in patients. The findings contribute to understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms of CLTA, TUBB, and FBXL5 in PMOP and may facilitate the development of novel therapeutic strategies and improved monitoring of the disease.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yue Tan, Yujing Wang, Qin Zhu, Yan Xue, Xuhao Ji, Zhenkun Li, Jiawen Shen, Chengming Sun, Shiqi Ren, Chenlin Zhang, Jianfeng Chen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









