Caffeine toxicity in zebrafish – Neurobehavioral changes, developmental defects, and oxidative stress: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13383Keywords:
Caffeine, zebrafish, neurobehavioral alterations, oxidative stress, developmental toxicityAbstract
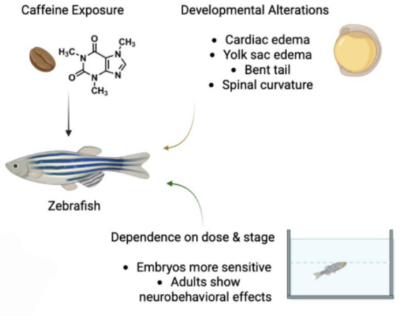
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive stimulants, primarily functioning as a non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist. Its increasing detection in wastewater and surface waters reflects extensive anthropogenic use. This review synthesizes evidence from zebrafish (Danio rerio)—a genetically tractable vertebrate with rapidly developing external embryos—to assess the impact of caffeine exposure across environmentally relevant (ng–µg/L) and pharmacological/toxicological (mg/L and above) concentrations on early development and neurobehavior. Behavioral studies indicate dose- and stage-dependent alterations in locomotion, anxiety-like responses, memory performance, and sleep patterns, suggesting disruptions in neural circuitry and stress-axis regulation. Biochemical analyses frequently reveal oxidative imbalances characterized by increased reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation, alongside changes in antioxidant defenses (e.g., glutathione levels, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and glutathione reductase activity). These findings support oxidative stress as a potential mechanistic hub, although a causal relationship has yet to be established. Embryonic exposure to caffeine is associated with developmental toxicity, including delayed hatching and concentration-dependent malformations such as edema, axial deformities, impaired angiogenesis, and neuromuscular defects at higher doses. However, cross-study comparisons are hindered by variations in units, exposure durations, and assay protocols. In summary, caffeine disrupts behavior, redox homeostasis, and developmental processes in zebrafish, highlighting the necessity for standardized methodologies to identify stage-specific vulnerabilities.
Citations
Downloads
References
Saraiva SM, Jacinto TA, Gonçalves AC, Gaspar D, Silva LR. Overview of Caffeine Effects on Human Health and Emerging Delivery Strategies. Pharmaceuticals. 2023;16(8):1067.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081067
Reddy VS, Shiva S, Manikantan S, Ramakrishna S. Pharmacology of caffeine and its effects on the human body. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports. 2024;100138.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmcr.2024.100138
Čižmárová B, Kraus V, Birková A. Caffeinated Beverages–Unveiling Their Impact on Human Health. Beverages. 2025;11(1):18.
https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11010018
Mahoney CR, Giles GE, Marriott BP, Judelson DA, Glickman EL, Geiselman PJ, et al. Intake of caffeine from all sources and reasons for use by college students. Clinical Nutrition. 2019;38.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.004
Mihaiescu T, Turti S, Souca M, Muresan R, Achim L, Prifti E, et al. Caffeine and Taurine from Energy Drinks–A Review. Cosmetics. 2024;11(1):12.
https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010012
Sharma B, Agriantonis G, Dawson-Moroz S, Brown R, Simon W, Ebelle D, et al. Caffeine: A Neuroprotectant and Neurotoxin in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). Nutrients. 2025;17(11):1925.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111925
Rauf MQ, Sharma L, Essiet E, Elhassan O, Fahim R, Irem-Oko F, et al. Caffeine Consumption Patterns, Health Impacts, and Media Influence: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.86215
Kolahdouzan M, Hamadeh MJ. The neuroprotective effects of caffeine in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12684
Alasmari F. Caffeine induces neurobehavioral effects through modulating neurotransmitters. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2020.02.005
Barcelos RP, Lima FD, Carvalho NR, Bresciani G, Royes LF. Caffeine effects on systemic metabolism, oxidative-inflammatory pathways, and exercise performance. Nutrition Research. 2020:1–17.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2020.05.005
Brent RL, Christian MS, Diener RM. Evaluation of the reproductive and developmental risks of caffeine. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2011.
https://doi.org/10.1002/bdrb.20288
Rembiałkowska N, Demiy A, Dąbrowska A, Mastalerz J, Szlasa W. Caffeine as a Modulator in Oncology: Mechanisms of Action and Potential for Adjuvant Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26(13):6252.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136252
Mielgo-Ayuso J, Marques-Jiménez D, Refoyo I, Del Coso J, León-Guereño P, Calleja-González J. Effect of caffeine supplementation on sports performance based on differences between sexes: A systematic review. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2313.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102313
Soós R, Gyebrovszki Á, Tóth Á, Jeges S, Wilhelm M. Effects of caffeine and caffeinated beverages in children, adolescents and young adults: Short review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(23):12389.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312389
Willson C. The clinical toxicology of caffeine: A review and case study. Toxicol Rep. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.11.002
Alsunni AA. Energy drink consumption: Beneficial and adverse health effects. International Journal of Health Science. 2015.
https://doi.org/10.12816/0031237
Song X, Singh M, Lee KE, Vinayagam R, Kang SG. Caffeine: A Multifunctional Efficacious Molecule with Diverse Health Implications and Emerging Delivery Systems. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(22):12003.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212003
Santos N, Picolo V, Domingues I, Perillo V, Villacis RAR, Grisolia CK, et al. Effects of environmental concentrations of caffeine on adult zebrafish behaviour: a short-term exposure scenario. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2023;30.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26799-4
Amar A, Ramachandran B. Environmental stressors differentially modulate anxiety-like behaviour in male and female zebrafish. Behavioural Brain Research. 2023;450:114470.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114470
Teame T, Zhang Z, Ran C, Zhang H, Yang Y, Ding Q, et al. The use of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as biomedical models. Animal Frontiers. 2019;9.
https://doi.org/10.1093/af/vfz020
Choi T-Y, Choi T-I, Lee Y-R, Choe S-K, Kim C-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53:310–7.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00571-5
Don DW, Choi T-I, Kim T-Y, Lee K-H, Lee Y, Kim C-H. Using zebrafish as an animal model for studying rare neurological disorders: A human genetics perspective. Journal of Genetic Medicine. 2024;21:6–13.
https://doi.org/10.5734/JGM.2024.21.1.6
Lee J, Freeman JL. Zebrafish as a model for developmental neurotoxicity assessment: The Application of the zebrafish in defining the effects of arsenic, methylmercury, or lead on early neurodevelopment. Toxics. 2014;2(3):464.
https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2030464
Bugel SM, Tanguay RL, Planchart A. Zebrafish: A Marvel of High-Throughput Biology for 21st Century Toxicology. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2014.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-014-0029-5
Félix L, Lobato-Freitas C, Monteiro SM, Venâncio C. 24-Epibrassinolide modulates the neurodevelopmental outcomes of high caffeine exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part - C: Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2021;249.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109143
Rosa LV, Ardais AP, Costa FV, Fontana BD, Quadros VA, Porciúncula LO, et al. Different effects of caffeine on behavioral neurophenotypes of two zebrafish populations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2018;165.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2017.12.002
Wei Y, Miao Z, Ye H, Wu M, Wei X, Zhang Y, et al. The Effect of Caffeine Exposure on Sleep Patterns in Zebrafish Larvae and Its Underlying Mechanism. Clocks Sleep. 2024;6:749–63.
https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep6040048
Wilson LC, Lyttle M, Kanan A, Le A. Social stimuli impact behavioral responses to caffeine in the zebrafish. Sci Rep. 2024;14.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80629-2
Yeh C-H, Liao Y-F, Chang C-Y, Tsai J-N, Wang Y-H, Cheng C-C, et al. Caffeine treatment disturbs the angiogenesis of zebrafish embryos. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2012;35:361–5.
https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2011.627864
Basnet RM, Zizioli D, Muscò A, Finazzi D, Sigala S, Rossini E, et al. Caffeine inhibits direct and indirect angiogenesis in zebrafish embryos. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4856.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094856
Clayman CL, Connaughton VP. Neurochemical and Behavioral Consequences of Ethanol and/or Caffeine Exposure: Effects in Zebrafish and Rodents. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;20.
https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X19666211111142027
de Farias NO, de Sousa Andrade T, Santos VL, Galvino P, Suares-Rocha P, Domingues I, et al. Neuromotor activity inhibition in zebrafish early-life stages after exposure to environmental relevant concentrations of caffeine. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. 2021;56:1306–15.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2021.1989931
dePaula J, Farah A. Caffeine Consumption through Coffee: Content in the Beverage, Metabolism, Health Benefits and Risks. Beverages. 2019;5(2):37.
https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5020037
Fiani B, Zhu L, Musch BL, Briceno S, Andel R, Sadeq N, et al. The Neurophysiology of Caffeine as a Central Nervous System Stimulant and the Resultant Effects on Cognitive Function. Cureus. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.15032
Boccuni I, Fairless R. Retinal Glutamate Neurotransmission: From Physiology to Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Retinal Ganglion Cell Degeneration. Life. 2022;12(5):638.
https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050638
Ősz BE, Jîtcă G, Ștefănescu RE, Pușcaș A, Tero-Vescan A, Vari CE. Caffeine and Its Antioxidant Properties–It Is All about Dose and Source. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):13074.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113074
Choi M-K, Ahn H-S, Kim D-E, Lee D-S, Park C-S, Kang C-K. Effects of Varying Caffeine Dosages and Consumption Timings on Cerebral Vascular and Cognitive Functions: A Diagnostic Ultrasound Study. Applied Sciences. 2025;15(4):1703.
https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041703
Echeverri D, Montes FR, Cabrera M, Galán A, Prieto A. Caffeine's vascular mechanisms of action. Int J Vasc Med. 2010.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/834060
Lopez-Garcia E, Van Dam RM, Li TY, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Hu FB. The relationship of coffee consumption with mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148.
https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-148-12-200806170-00003
Bolignano D, Coppolino G, Barillà A, Campo S, Criseo M, Tripodo D, et al. Caffeine and the Kidney: What Evidence Right Now? Journal of Renal Nutrition. 2007;17.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2007.02.006
Rodak K, Kokot I, Kratz EM. Caffeine as a factor influencing the functioning of the human body-friend or foe? Nutrients. 2021;13(9):3088.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093088
Blechman J, Levkowitz G, Gothilf Y. The not-so-long history of zebrafish research in Israel. International Journal of Developmental Biology. 2017;61.
https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.160346gl
Santos N, Picolo V, Domingues I, Sousa-Moura D, Grisolia CK, Oliveira M. Behavioral and biochemical effects of environmental concentrations of caffeine in zebrafish after long-term exposure. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. 2024;59:453–65.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2024.2420482
Alia AO, Petrunich-Rutherford ML. Anxiety-like behavior and whole-body cortisol responses to components of energy drinks in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PeerJ. 2019;2019.
https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7546
Li Y, Yan Z, Lu Z, Li K. Zebrafish gender-specific anxiety-like behavioral and physiological reactions elicited by caffeine. Behavioural Brain Research. 2024;472:115151.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115151
Nair JS, Olary L, Sivarajan D, Amar A, Ramachandran B. Caffeine bidirectionally regulates social preference and anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish. Brazilian Journal of Development. 2025;11:e81087.
https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n7-049
Fontana BD, Parker MO. The larval diving response (LDR): Validation of an automated, high-throughput, ecologically relevant measure of anxiety-related behavior in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Neurosci Methods. 2022;381.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109706
Rodrigues S, Alves RS, Antunes SC. Impact of Caffeine on Aquatic Ecosystems: Assessing Trophic-Level Biological Responses. J Xenobiot. 2025;15(3):86.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15030086
Li S, Wen J, He B, Wang J, Hu X, Liu J. Occurrence of caffeine in the freshwater environment: Implications for ecopharmacovigilance. Environmental Pollution. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114371
Santos N, Oliveira M, Domingues I. Influence of exposure scenario on the sensitivity to caffeine. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023;30.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30945-3
Maeda H, Hasumi A, Yoshida K ichi. Caffeine-induced bradycardia, death, and anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish larvae. Forensic Toxicol. 2021;39.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-021-00577-8
Richendrfer H, Pelkowski SD, Colwill RM, Creton R. On the edge: Pharmacological evidence for anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish larvae. Behavioural Brain Research. 2012;228.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.11.041
De Carvalho TS, Cardoso PB, Santos-Silva M, Lima-Bastos S, Luz WL, Assad N, et al. Oxidative Stress Mediates Anxiety-Like Behavior Induced by High Caffeine Intake in Zebrafish: Protective Effect of Alpha-Tocopherol. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8419810
Tan JK, Nazar FH, Makpol S, Teoh SL. Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules. 2022;27(21):7374.
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217374
Tazkia AA, Nugraha ZS. The Effect of Caffeine towards Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Juvenile Working Memory Exposed by Unpredictable Chronic Stress (UCS). 2021.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0010490202080213
Ruiz-Oliveira J, Silva PF, Luchiari AC. Coffee time: Low caffeine dose promotes attention and focus in zebrafish. Learn Behav. 2019;47.
https://doi.org/10.3758/s13420-018-0369-3
Santos LC, Ruiz-Oliveira J, Silva PF, Luchiari AC. Caffeine Dose–Response Relationship and Behavioral Screening in Zebrafish. The Question of Caffeine. 2017.
https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.68341
Daly JW, Shi D, Nikodijevic O, Jacobson KA. The role of adenosine receptors in the central action of caffeine HHS Public Access. 1994.
Allada R, Cirelli C, Sehgal A. Molecular Mechanisms of Sleep Homeostasis in Flies and Mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9:a027730.
https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a027730
Benoit E, Lyons DG, Rihel J. Noradrenergic tone is not required for neuronal activity-induced rebound sleep in zebrafish. J Comp Physiol B. 2024;194.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-023-01504-6
Ross JA, Van Bockstaele EJ. The Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System in Stress and Arousal: Unraveling Historical, Current, and Future Perspectives. Front Psychiatry. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.601519
Zhdanova I V. Sleep and its regulation in zebrafish. Rev Neurosci. 2011;22.
https://doi.org/10.1515/RNS.2011.005
Kazimi N, Cahill GM. Development of a circadian melatonin rhythm in embryonic zebrafish. Developmental Brain Research. 1999;117.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-3806(99)00096-6
Tran TDT, Park J, Kim DY, Han IO. Caffeine-induced protein kinase A activation restores cognitive deficits induced by sleep deprivation by regulating O-GlcNAc cycling in adult zebrafish. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024;326.
https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00691.2023
Bailey J, Oliveri A, Levin ED. Zebrafish model systems for developmental neurobehavioral toxicology. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013.
https://doi.org/10.1002/bdrc.21027
Santoriello C, Zon LI. Hooked! modeling human disease in zebrafish. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2012.
https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI60434
Chen YH, Huang YH, Wen CC, Wang YH, Chen WL, Chen LC, et al. Movement disorder and neuromuscular change in zebrafish embryos after exposure to caffeine. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2008;30.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2008.04.003
Chakraborty C, Hsu CH, Wen ZH, Lin CS, Agoramoorthy G. Effect of caffeine, norfloxacin and nimesulide on heartbeat and VEGF expression of zebrafish larvae. J Environ Biol. 2011;32.
Martini D, Del Bo' C, Tassotti M, Riso P, Rio D Del, Brighenti F, et al. Coffee consumption and oxidative stress: A review of human intervention studies. Molecules. 2016;21(8):979.
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080979
Gülçin İ. In vitro prooxidant effect of caffeine. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2008;23:149–52.
https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360701306404
Agudelo-Ochoa GM, Pulgarín-Zapata IC, Velásquez-Rodriguez CM, Duque-Ramírez M, Naranjo-Cano M, Quintero-Ortiz MM, et al. Coffee consumption increases the antioxidant capacity of plasma and has no effect on the lipid profile or vascular function in healthy adults in a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Nutrition. 2016;146.
https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.115.224774
Moura-Nunes N, Perrone D, Farah A, Donangelo CM. The increase in human plasma antioxidant capacity after acute coffee intake is not associated with endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidant components. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2009;60:173–81.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09637480903158893
Natella F, Nardini M, Giannetti I, Dattilo C, Scaccini C. Coffee drinking influences plasma antioxidant capacity in humans. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jf025768c
Corrêa TAF, Monteiro MP, Mendes TMN, de Oliveira DM, Rogero MM, Benites CI, et al. Medium Light and Medium Roast Paper-Filtered Coffee Increased Antioxidant Capacity in Healthy Volunteers: Results of a Randomized Trial. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition. 2012;67.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-012-0297-x
Kotyczka C, Boettler U, Lang R, Stiebitz H, Bytof G, Lantz I, et al. Dark roast coffee is more effective than light roast coffee in reducing body weight, and in restoring red blood cell vitamin E and glutathione concentrations in healthy volunteers. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011;55.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201100248
Bakuradze T, Boehm N, Janzowski C, Lang R, Hofmann T, Stockis JP, et al. Antioxidant-rich coffee reduces DNA damage, elevates glutathione status and contributes to weight control: Results from an intervention study. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011;55.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201100093
Esposito F, Morisco F, Verde V, Ritieni A, Alezio A, Caporaso N, et al. Moderate coffee consumption increases plasma glutathione but not homocysteine in healthy subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01429.x
Hoelzl C, Knasmüller S, Wagner KH, Elbling L, Huber W, Kager N, et al. Instant coffee with high chlorogenic acid levels protects humans against oxidative damage of macromolecules. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201000048
Mišík M, Hoelzl C, Wagner K-H, Cavin C, Moser B, Kundi M, et al. Impact of paper filtered coffee on oxidative DNA-damage: Results of a clinical trial. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis. 2010;692:42–8.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.08.003
Abdelkader TS, Chang SN, Kim TH, Song J, Kim DS, Park JH. Exposure time to caffeine affects heartbeat and cell damage-related gene expression of zebrafish Danio rerio embryos at early developmental stages. Journal of Applied Toxicology. 2013;33.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2787
Diogo BS, Antunes SC, Pinto I, Amorim J, Teixeira C, Teles LO, et al. Insights into environmental caffeine contamination in ecotoxicological biomarkers and potential health effects of Danio rerio. Heliyon. 2023;9.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19875
Lu PZ, Lai CY, Wen-Hsiung C. Caffeine induces cell death via activation of apoptotic signal and inactivation of survival signal in human osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2008;9.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9050698
Gonçalves DF, Senger LR, Foletto JVP, Michelotti P, Soares FAA, Dalla Corte CL. Caffeine improves mitochondrial function in PINK1 B9-null mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023;55.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-022-09952-5
Kanlaya R, Subkod C, Nanthawuttiphan S, Thongboonkerd V. Caffeine causes cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 and increases of ubiquitinated proteins, ATP and mitochondrial membrane potential in renal cells. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.09.023
Wang L tao, He P cheng, Li A qi, Cao K xiang, Yan J wei, Guo S, et al. Caffeine promotes angiogenesis through modulating endothelial mitochondrial dynamics. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42.
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Cătălina Ionescu, Petru-Fabian Lungu, Viorica Rarinca, Malina Visternicu, Alin Ciobica, Vasile Burlui, Cristina Albert, Mircea-Nicusor Nicoara, Gabriel-Ionut Plavan, Bogdan Novac, Bogdan Gurzu, Daniela Ivona Tomița

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









