Chromogranin A Detection in Saliva of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2010.2725Keywords:
Chromogranin A, diabetes type 2, innate immunity salivaAbstract
Chromogranin A is present in secretion granules of nerve, endocrine and immune cells and is a precursor of several peptides with antibacterial and antifungal properties at micromolar concentrations.
Our aim in this prospective, double blind study, was to determine the expression of chromogranin A and its peptides at protein level in saliva of type 2 diabetic patients and thereby to obtain a new non-invasive diagnostic means for the future.
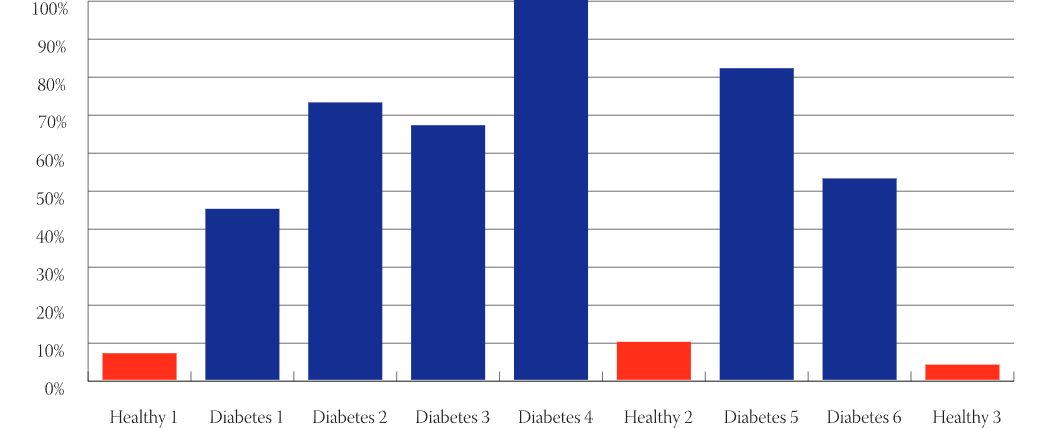
Saliva was taken from 30 type 2 diabetic patients and 30 healthy individuals at the same time interval in the morning without any oral stimuli. Circadianic periodics in protein productions have been avoided. The presence of chromogranin A and its derived peptides was determined in whole saliva, after centrifugation at 4°C for 12 min at 14 000 rpm, by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Immunoblotting (Western Blot). To ensure same protein concentrations Bradford protein quantification assay has been performed before.
For the first time, we have determined an overexpression of chromogranin A in saliva of diabetic patients in 100% of the individuals.
Chromogranin A, a circulating biomarker for epithelial tumours, is also overexpressed in saliva of type 2 diabetic patients. To confirm our results, more studies with a large amount of patients is necessary.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-11-28
Published 2010-02-20









