Characteristics of Symptomatic Epilepsy in Patients with Brain Tumours
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2009.2862Keywords:
symptomatic epilepsy, brain tumoursAbstract
The aim of our work is to determine the total number, age, gender of the patients with the symptomatic epileptic seizures associated with brain tumours, tumour location, clinical signs and characteristics of epileptic seizures. We have analyzed medical documentation of the patients with brain tumours hospitalized at the Department of Neurology, University of Sarajevo Clinics Centre. This study is retrospective and includes time period from 1st January 2000 until 31st December 2005.
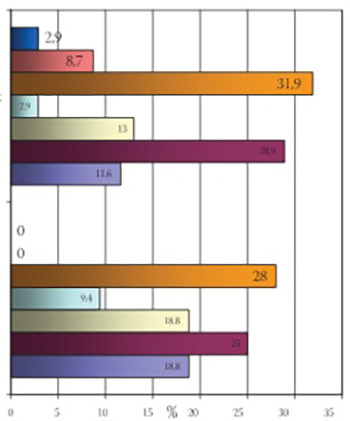
During the observed period at the Department of Neurology in Sarajevo there were in total 9753 hospitalized patients, from which 101 (1,1%) patients with the brain tumour diagnosis. Average patient’s age was 62,60 ± 1,28 years. In one third of the patients (32%) were recorded epileptic seizures, without significant difference between genders. In case of symptomatic epilepsy, significantly more frequent locations of tumours were: in several lobes (28%), parietal lobe (25%), as well as frontal and temporal lobe (18,8% each), while there were no changes in cerebellum and brain stem (χ2 =7,174, p<0,05).
The most prominent signs of illness in our sample were hemiparesis with the cranial nerves lesion (56,3%), speech problems (25%). Normal neurologic findings were significantly more frequent among patients with the symptomatic epilepsy (χ2 =6,349, p<0,05). The most often was a single seizure (59%), in 38% of cases there were recorded series of seizures, and only 3% of patients had status epilepticus. In relation to the type of seizures, the most often are simple partial seizures with or without secondary generalization (66%), than generalized convulsive (31%), and the rarest one are complex partial seizures (3%).
Symptomatic epilepsy in case of brain tumours occurs in one third of patients, at older age, and in both genders. The lesion usually affects several lobes and cause simple partial seizures with or without secondary generalization. The most often clinical signs in case of all brain tumours are cranial nerves lesion and hemiparesis, while the normal neurologic findings are significantly dominant in the group of patients with the epileptic seizures.
Citations
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-12-19
Published 2009-02-20









