Analysis of multidrug-resistant bacteria in 3223 patients with hospital-acquired infections (HAI) from a tertiary general hospital in China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2018.3826Keywords:
Multidrug-resistant bacteria, infection, distribution, intensive care unit, MDR, nosocomial infections, hospital-acquired infections, HAIAbstract
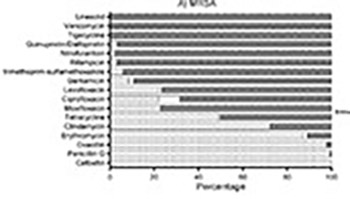
The frequency of antimicrobial resistance has increased globally due to misuse and overuse of antibiotics, and multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria are now recognized as a major cause of hospital-acquired infections (HAI). Our aim was to investigate the prevalence, distribution, and antimicrobial susceptibility rates of MDR bacteria in patients with HAI from a tertiary hospital in China. We retrospectively evaluated all patients with a confirmed diagnosis of bacterial infection at a tertiary general hospital in Jining, for the period between January 2012 and December 2014. The following clinical and demographic data were collected: age, sex, specimens, treatment, microbiology results, and antibiotic resistance patterns of isolates. Bacterial identification and susceptibility testing were performed using VITEK 2 COMPACT system. We screened a total of 15,588 patients, out of which 7579 (48.6%) had an HAI. MDR showed 3223 out of 7579 isolates (42.5%). The most frequently isolated MDR bacteria in patients with HAI were extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli (n = 1216/3223, 37.7%), MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 627/3223, 19.5%) and MDR Acinetobacter baumannii (n = 588/3223, 18.2%). MDR-HAI were more common in males (2074/3223, 64.4%) and in elderly patients (≥60 years; 1196/3223, 37.1%). Sputum was the main source of MDR isolates (2056/3223, 63.8%). Patients with MDR-HAI were predominantly distributed in different types of intensive care units. MDR strains in our study showed resistance to most current antibiotics. Overall, patients with HAI infections attributed to MDR bacteria were widely distributed in our hospital. Enhanced surveillance of MDR bacteria is critical for guiding the rational use of antibiotics and reducing the incidence of HAI.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-09-14
Published 2019-02-12









