A key bacterial cytoskeletal cell division protein FtsZ as a novel therapeutic antibacterial drug target
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4597Keywords:
FtsZ, multidrug resistance, cell division, antimicrobial, inhibitors, natural antimicrobial compoundsAbstract
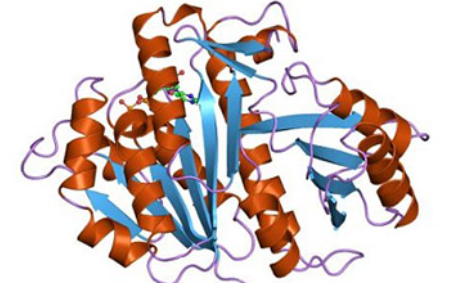
Nowadays, the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacterial strains initiates the urgent need for the elucidation of the new drug targets for the discovery of antimicrobial drugs. Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z (FtsZ), a eukaryotic tubulin homolog, is a GTP-dependent prokaryotic cytoskeletal protein and is conserved among most bacterial strains. In vitro studies revealed that FtsZ self-assembles into dynamic protofilaments or bundles and forms a dynamic Z-ring at the center of the cell in vivo, leading to septation and consequent cell division. Speculations on the ability of FtsZ in the blockage of cell division make FtsZ a highly attractive target for developing novel antibiotics. Researchers have been working on synthetic molecules and natural products as inhibitors of FtsZ. Accumulating data suggest that FtsZ may provide the platform for the development of novel antibiotics. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the properties of FtsZ protein and bacterial cell division, as well as in the development of FtsZ inhibitors.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Mujeeb Rahman, Ping Wang, Na Wang, Yaodong Chen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-01-25
Published 2020-08-03









