Effect of topically applied sildenafil citrate on wound healing: experimental study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2014.3.48Keywords:
Wound healing, Sildenafil Citrate, cGMPAbstract
Wound healing is a complex process that necessitates organization of different cell types and several signalling molecules. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of different concentrations of sildenafil citrate, which decreases cGMP degradation, on wound healing by secondary intention.
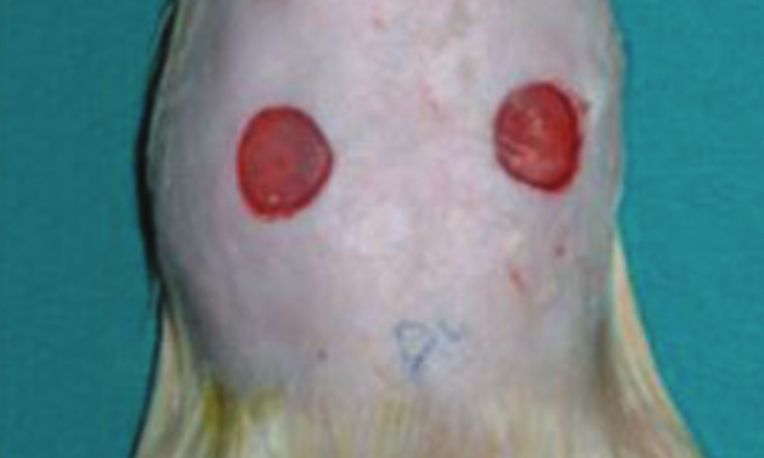
This study was performed using 25 Sprague Dawley rats weighing 200-250 grams. 4 dorsal defects were created. Four different treatment modalities which were 1% and 5% sildenafil citrate gel prepared with carbopol, pure carbopol gel without any drug in it and 0,9% NaCl solution; were applied to each lesion of the same rat. Randomly selected five rats (25 rats in total) were sacrificed on 3rd, 5th, 7th, 10th, and 14th days; and the effect of each modality was evaluated by means of defect area measurement, histopathological examination and measurement of tissue hydroxyproline levels.
Sildenafil citrate gel application decreased the defect areas in a dose independent manner starting from 3rd day and dose dependent manner after 7th day. By means of vascularization, sildenafil citrate increased vascularity starting from 3rd day. The strength of acute inflammation was superior in sildenafil groups starting from 5th day; and the amount and maturation of granulation in the wound bed, as well as the strength of chronic inflammation were superior in defects treated with sildenafil citrate as early as 7th day.
Citations
Downloads
References
REFERENCES
Salcido RS. Viagra and wound healing: the NO connection. Advances in skin & wound care. 2008;21(3):106, 8-9.
Wimalawansa SJ. Nitric oxide: new evidence for novel therapeutic indications. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(11):1935-54.
Filippin LI, Cuevas MJ, Lima E, Marroni NP, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Xavier RM. Nitric oxide regulates the repair of injured skeletal muscle. Nitric oxide : biology and chemistry. 2011;24(1):43-9.
Efron DT, Most D, Barbul A. Role of nitric oxide in wound healing. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2000;3(3):197-204.
Schaffer MR, Tantry U, Gross SS, Wasserburg HL, Barbul A. Nitric oxide regulates wound healing. J Surg Res. 1996;63(1):237-40.
Lee RH, Efron D, Tantry U, Barbul A. Nitric oxide in the healing wound: a time-course study. J Surg Res. 2001;101(1):104-8.
Farsaie S, Khalili H, Karimzadeh I, Dashti-Khavidaki S. An old drug for a new application: potential benefits of sildenafil in wound healing. Journal of pharmacy & pharmaceutical sciences : a publication of the Canadian Society for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Societe canadienne des sciences pharmaceutiques. 2012;15(4):483-98.
Corbin JD, Francis SH. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase-5: target of sildenafil. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(20):13729-32.
Michell BJ, Chen Z, Tiganis T, Stapleton D, Katsis F, Power DA, et al. Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(21):17625-8.
Sanchez FA, Rana R, Gonzalez FG, Iwahashi T, Duran RG, Fulton DJ, et al. Functional significance of cytosolic endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS): regulation of hyperpermeability. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(35):30409-14.
Shabani M, Pulfer SK, Bulgrin JP, Smith DJ. Enhancement of wound repair with a topically applied nitric oxide-releasing polymer. Wound Repair Regen. 1996;4(3):353-62.
Barral SM, Araujo ID, Vidigal PV, Mayrink CA, Araujo AD, Costa PR. Effects of sildenafil on the viability of random skin flaps. Acta cirurgica brasileira / Sociedade Brasileira para Desenvolvimento Pesquisa em Cirurgia. 2011;26(4):314-9.
Ayten R, Cetinkaya Z, Girgin M, Ozercan I, Ustundag B, Aygen E. The effects of intraperitoneal sildenafil administration on healing of left colonic anastomoses and intra-abdominal adhesion formation in the presence of intra-abdominal infection. Diseases of the colon and rectum. 2008;51(12):1837-41.
Histing T, Marciniak K, Scheuer C, Garcia P, Holstein JH, Klein M, et al. Sildenafil accelerates fracture healing in mice. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2011;29(6):867-73.
Derici H, Kamer E, Unalp HR, Diniz G, Bozdag AD, Tansug T, et al. Effect of sildenafil on wound healing: an experimental study. Langenbeck's archives of surgery / Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chirurgie. 2010;395(6):713-8.
Farsaei S, Khalili H, Farboud ES, Khazaeipour Z. Sildenafil in the treatment of pressure ulcer: a randomised clinical trial. International wound journal. 2013.
Pingarron-Martin L, Arias-Gallo LJ. Sildenafil effect on prevention of thrombosis after microsurgical anastomosis: experimental rat model of thrombotic suture. Oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2013.
Gravvanis A, Papalois A, Delikonstantinou I, Pentilas N, Zogogiannis I, Tsoutsos D, et al. Changes in arterial blood flow of free flaps after the administration of sildenafil in swine. Microsurgery. 2011;31(6):465-71.
Mutschler W. [Physiology and pathophysiology of wound healing of wound defects]. Der Unfallchirurg. 2012;115(9):767-73.
Gethin G. Understanding the inflammatory process in wound healing. British journal of community nursing. 2012;Suppl:S17-8, S20, S2.
Daff S. NO synthase: structures and mechanisms. Nitric oxide : biology and chemistry. 2010;23(1):1-11.
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Marc Rhoads J, et al. Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino acids. 2009;37(1):153-68.
Glossman H, Petrischor, G., Bartsch, G. Molecular mechanisms of the effects of sildenafil (Viagra). Exp Gerontol. 1999;34:305-18.
Arbss MA, Ferrando JM, Vidal J, Quiles MT, Huguet P, Castells J, et al. Early effects of exogenous arginine after the implantation of prosthetic material into the rat abdominal wall. Life Sci. 2000;67(20):2493-512.
Kavalukas SL, Uzgare AR, Bivalacqua TJ, Barbul A. Arginase inhibition promotes wound healing in mice. Surgery. 2012;151(2):287-95.
Debats IB, Wolfs TG, Gotoh T, Cleutjens JP, Peutz-Kootstra CJ, van der Hulst RR. Role of arginine in superficial wound healing in man. Nitric oxide : biology and chemistry / official journal of the Nitric Oxide Society. 2009;21(3-4):175-83.
Yamasaki K, Edington HD, McClosky C, Tzeng E, Lizonova A, Kovesdi I, et al. Reversal of impaired wound repair in iNOS-deficient mice by topical adenoviral-mediated iNOS gene transfer. J Clin Invest. 1998;101(5):967-71.
Most D, Efron DT, Shi HP, Tantry US, Barbul A. Characterization of incisional wound healing in inducible nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Surgery. 2002;132(5):866-76.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2015 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2014-07-27
Published 2014-08-16









