Pharmacogenetics of new classes of antidiabetic drugs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.5646Keywords:
Type 2 diabetes, pharmacogenetics, personalized medicine, new antidiabeticsAbstract
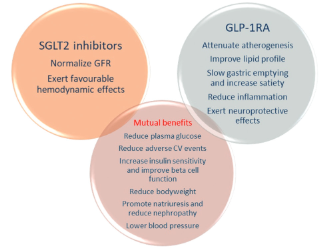
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) has a continuously rising prevalence worldwide. Pharmacogenetics has been recognized as a promising concept for pharmacological treatment of T2D, as antidiabetic drugs are not equally effective and safe for all patients, and the costs of diabetes treatment are increasing. The latest published guidelines on T2D treatment firmly endorse the use of newer antidiabetic drugs, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-IVi), and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), considering their satisfactory pharmacological effect and good safety profile. Furthermore, SGLT2i and GLP-1RA show protective effects in patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. However, there has been growing evidence that the effectiveness and safety of these drug classes could depend on genetic variability. Here, we summarized the results of the published studies on the pharmacogenetic biomarkers for the three drug classes. A number of genetic variations have been investigated so far. The explored candidate genes mostly encode drug targets, drug-metabolizing enzymes, and genes linked to T2D risk. Although many of the results are promising, it is still necessary to obtain more information from larger controlled studies to confirm their clinical significance. This approach may lead towards more personalized treatment for patients with T2D.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Selma Imamovic Kadric, Aida Kulo Cesic, Tanja Dujic

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-04-19
Published 2021-12-01









