Hepatoprotective effect of taxifolin on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in mice: Involvement of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8743Keywords:
Flavonoids, cyclophosphamide, inflammation, taxifolin, hepatotoxicity, oxidative damage, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)Abstract
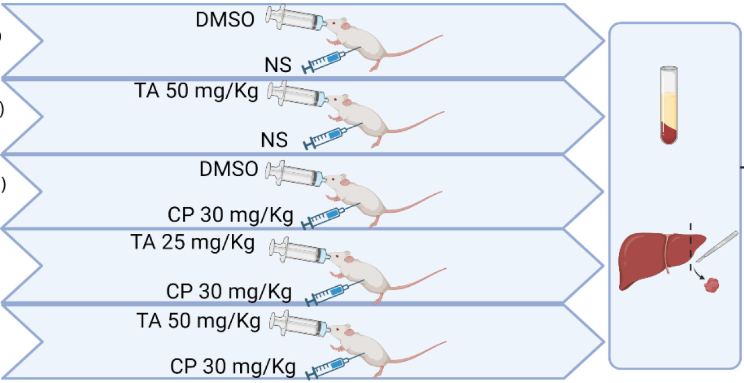
Taxifolin (TA) is a natural flavonoid found in many foods and medicinal plants with well-documented antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Cyclophosphamide (CP) is an effective antineoplastic and immunosuppressive agent; however, it is associated with numerous adverse events, including hepatotoxicity. Herein, we aimed to investigate the potential protective effects of TA using a mouse model of CP-induced hepatotoxicity. Mice were co-treated with TA (25 and 50 mg/kg, orally) and CP (30 mg/kg, i.p.) for 10 consecutive days and sacrificed 24 hours later. CP induced increased transaminases (ALT and AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) paralleled with pronounced histopathological alterations in the liver. Moreover, hepatic tissues of CP-injected mice showed increased malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonyl, and nitric oxide (NO) levels, accompanied by decreased antioxidant defenses (glutathione [GSH], superoxide dismutase [SOD], and catalase [CAT]). Livers of CP-injected mice also showed increased inflammatory response (nuclear transcription factor kappa-B [NF-κB] p65 activation, increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α], interleukin 1 beta [IL-1β], and IL-6) and apoptosis (decreased Bcl-2 and increased Bax and caspase-3 expression levels). Remarkably, TA ameliorated markers of liver injury and histological damage in CP-injected mice. TA treatment also attenuated numerous markers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in the liver of CP-injected mice. This was accompanied by increased nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) expression in the liver tissues of CP-injected mice. Taken together, this study indicates that TA may represent a promising new avenue to prevent/treat CP-induced hepatotoxicity and perhaps other liver diseases associated with oxidative stress and inflammation.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Osama Y. Althunibat, Mohammad H. Abukhalil, Muthana M. Jghef , Manal A. Alfwuaires, Abdulmohsen I. Algefare, Bader Alsuwayt, Reem Alazragi, Mohammed A. S. Abourehab, Afaf F. Almuqati, Shaik Karimulla, Saleem H. Aladaileh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-01-23
Published 2023-07-03









