Clinical characteristics associated with recurrent viral RNA positivity in patients within two weeks after recovering from the first SARS-CoV-2 infection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9661Keywords:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), recurrent viral RNA positivity (RP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR)Abstract
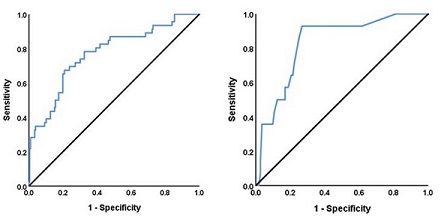
Many studies have shown that recovered coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients frequently exhibit recurrent viral RNA positivity (RP) for the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Our study aimed to summarize the clinical characteristics of these patients and explore potential reasons for RP occurrence. We divided 439 participants into four groups based on the severity of illness prior to the COVID-19 recovery and age: mild-child group, moderate-child group, mild-adult group, and moderate-adult group. Laboratory data were collected and statistically analyzed using the SPSS software, version 24.0. Significant differences were observed in age, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) levels between the mild-adult group and the moderate-adult group (P < 0.05). Additionally, AST levels differed significantly between the mild-child group and the moderate-child group (P < 0.05). The proportion of RP patients within the four groups varied from 7.95% to 26.13% within a 2-week period. Logistic regression analysis revealed that younger age and moderate symptoms were risk factors for RP in children, while the presence of comorbidities (such as chronic heart, lung, liver, and kidney diseases), elevated IL-6 levels, and NLR were risk factors for RP in adults. We constructed two predictive models containing these relevant parameters, and the results of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves indicated strong predictive utility. Our findings suggest that younger children with more severe symptoms, as well as adult patients with elevated levels of IL-6 and NLR and underlying diseases, are at higher risk of RP occurrence.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Xi Cao, Yongli Xie, Chunlei Zhou, Hong Mu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-09-05
Published 2024-01-03









