Sirtuin 1, as a potential prognosis marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma, regulates lipid metabolism and immune infiltration
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10304Keywords:
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), Sirutin 1 (Sirt1), prognosis, lipid metabolism disorder, immune infiltrationAbstract
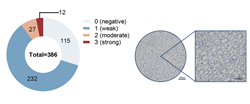
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a malignancy with a dismal prognosis, caused by the buildup of fat and glycogen. Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) is a deacetylase that regulates lipid metabolism. In this study, we collected tumor and paracancer tissues from 386 ccRCC patients and followed their prognosis over an extended time period. The expression of Sirt1 in these tissues was assessed using immunohistochemistry, and LinkedOmics database analysis identified differentially expressed genes associated with Sirt1. The survival curve was generated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and immune infiltration was analyzed using the Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) web tool. Our findings revealed that Sirt1 was expressed in tumor tissues, but not in normal tissues, and its high expression was associated with a worse prognosis. Furthermore, we observed a positive correlation between high Sirt1 expression and perirenal fat invasion and necrosis, leading to poorer survival outcomes. We established a nomogram to predict prognosis, and a correlation was observed with immune infiltration. In conclusion, our results suggest that high Sirt1 expression is associated with lipid metabolism disorder and immune infiltration, ultimately contributing to a dismal prognosis in ccRCC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
The authenticity of this article has been validated by uploading the key raw data onto the Research
Data Deposit platform (www.researchdata.org.cn), with the approval RDD number as RDDA2024689760.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Xuefei Wang, Fangqi Deng, Jiexi Liu, Jiayu Wang, Qing Chen, Jiabin Lu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









