Advances in PGD2/PTGDR2 signaling pathway in tumors: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10485Keywords:
Prostaglandins (PGs), prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), prostaglandin D2 receptor (PTGDR2), inflammation, cancer, signaling pathwayAbstract
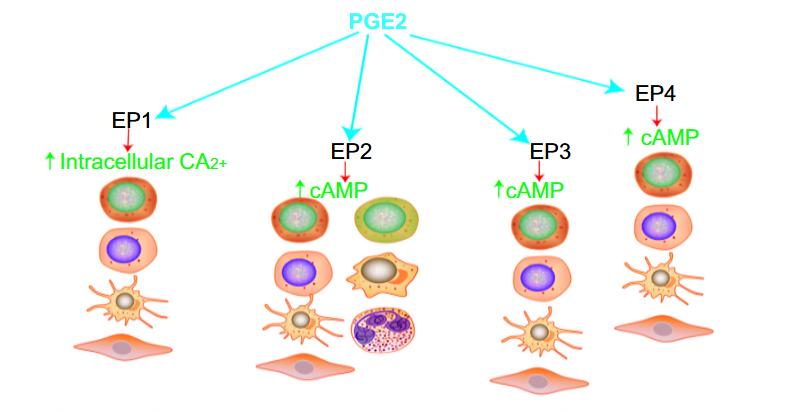
Studies have shown that the prostaglandin (PG) family acts as an allergic inflammatory mediator in malignant diseases. Furthermore, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and its related receptors, as well as the prostaglandin D2 (PGD2)/PGD2 receptor (PTGDR2), play irreplaceable roles in tumorigenesis and anti-tumor therapy. Several experiments have demonstrated that PGD2 signaling through PTGDR2 not only directly inhibits cancer cell survival, proliferation, and migration but also reduces resistance toward conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Recent studies from our and other laboratories have shown that PGD2, its ligands, and related metabolites can significantly alter the tumor microenvironment (TME) by promoting the secretion of chemokines and cytokines, thereby inhibiting tumor progression. Additionally, reduced PGD2 expression has been associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric, breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers, validating the preclinical findings and their clinical relevance. This review focuses on the current understanding of PGD2/PTGDR2 expression patterns and biological activity in cancer, proposing questions to guide the assessment of PGD2 and its receptors as potential targets for effective cancer therapies.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hengjin Tian, Kunpeng Ge, Lulu Wang, Peiyao Gao, Amin Chen, Feifan Wang, Fangzheng Guo, FengChao Wang, Qiang Zhang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









