Clinical significance of a novel inflammatory-nutritional index in glaucoma severity evaluation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12374Keywords:
Glaucoma, albumin, Alb, lymphocyte rate, biomarker, systemic inflammationAbstract
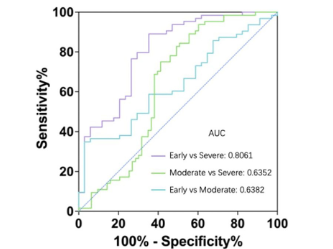
This study investigated the association between glaucoma and serum albumin (Alb), lymphocyte percentage (LYMPH%), and their combined index (LAP = LYMPH% × Alb), to evaluate their potential as biomarkers for systemic inflammation and disease progression in glaucoma. We enrolled 161 glaucoma patients and 181 healthy controls. Serum Alb and LYMPH% were measured using standard blood biochemistry and routine tests, and LAP was calculated accordingly. Statistical analyses were performed to compare these markers between groups and assess their correlation with disease severity. Both the median serum Alb level and peripheral blood LYMPH% were significantly lower in the glaucoma group compared to controls (Alb: 43.48 g/L vs 44.63 g/L, P < 0.001; LYMPH%: 24.25% vs 29.12%, P < 0.001). Correspondingly, LAP levels were also significantly reduced in glaucoma patients (1053 vs 1298, P < 0.001). Lower LYMPH% and LAP levels were associated with more severe glaucomatous visual impairment (LAP, healthy controls vs glaucoma: AUC = 0.7080, P < 0.001, Max Youden = 0.3621; early vs severe glaucoma: AUC = 0.8061, P < 0.001, Max Youden = 0.5377). In summary, LAP may serve as a supportive biomarker of systemic inflammation in glaucoma. It demonstrates good accuracy in reflecting glaucoma severity and shows potential for monitoring disease progression.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Xiao Xiao, Yanping Gao, Gao Zhang, Zuo Wang, An Li, Donghua Liu, Jing Fu, Wenbo Xiu, Chang Lu, Jinxia Wang, Xiong Zhu, Yang Chen, Lingling Chen, Bolin Deng, Ping Shuai, Chong He, Fang Lu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









