WFDC3 identified as a prognostic and immune biomarker in pancreatic cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12444Keywords:
Pancreatic cancer, whey acidic protein four-disulfide core, WFDC3, bioinformatics, metastasis, immunotherapy, prognosisAbstract
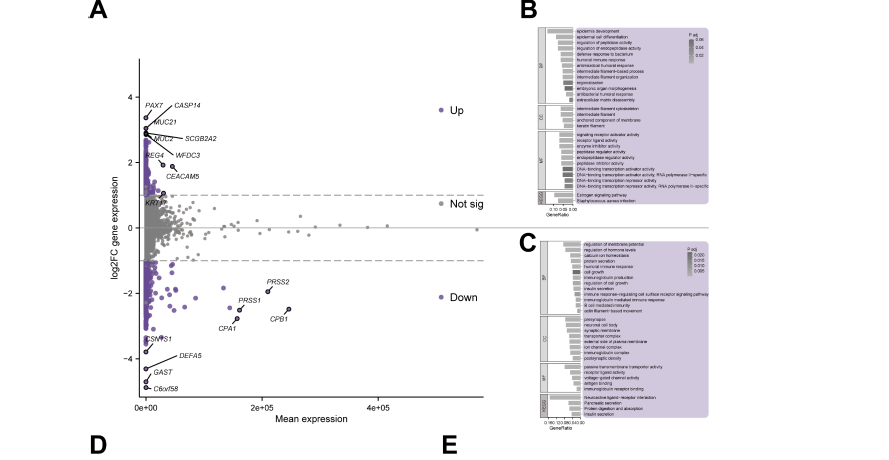
The whey acidic protein four-disulfide core (WFDC) family comprises key modulators of tumor initiation and progression, offering significant potential for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications. However, the specific role of WFDCs in the oncogenesis of pancreatic cancer (pancreatic adenocarcinoma [PAAD]) remains incompletely understood. To address this, we conducted an initial investigation using comprehensive bioinformatic analyses to evaluate WFDCs expression patterns across multiple tumor types, with a focus on PAAD. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from the TCGA and GEO repositories were analyzed to assess WFDC3 expression in PAAD tissues. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was employed to determine the prognostic significance of WFDC3. To explore its biological functions and underlying mechanisms, we performed functional enrichment analyses in combination with immune infiltration assessments. Experimental validation included CCK-8 and EdU proliferation assays, transwell migration and invasion tests, immunofluorescence staining, flow cytometry, LDH release assays, Western blotting, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR. A LASSO regression model was also developed to predict PAAD outcomes. Our findings reveal that WFDCs exhibit context-dependent roles in tumor progression. Specifically, WFDC3 expression was significantly elevated in PAAD and associated with poorer patient prognosis. Functionally, WFDC3 promoted PAAD cell metastasis by inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition and contributed to immune evasion by suppressing T cell cytotoxicity. In conclusion, our study identifies WFDC3 as a pro-oncogenic factor in PAAD progression, highlighting its potential as both a prognostic biomarker and a therapeutic target for regulating metastasis and immune responses in this malignancy.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bohan Liu, Xuqing Shi, Tianqi Liu, Huanwen Wu, Zhiyong Liang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









