Review of roles of RNA-binding proteins on NAFLD and the related pharmaceutical measures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12465Keywords:
RNA binding proteins, RBP, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD, therapy, mechanismAbstract
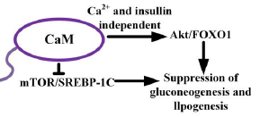
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease worldwide and poses a serious threat to public health. NAFLD is considered a risk factor for metabolic syndrome (MS) and is closely associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular disease. Recently, increasing attention has been paid to the role of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. A growing body of research has linked RBPs—such as human antigen R (HuR), sequestosome 1 (p62), polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTBP1), and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs)—to lipogenesis and inflammation, both of which contribute to NAFLD through mechanisms involving transcriptional regulation, alternative splicing, RNA stability, polyadenylation, and subcellular localization. However, these findings are often fragmented and lack a comprehensive synthesis. The interactions and mechanisms between RBPs and NAFLD have not yet been thoroughly reviewed. This article provides an overview of the roles and mechanisms of various RBPs in NAFLD, summarizing current knowledge with the aid of figures and tables. In particular, it highlights the influence of HuR on NAFLD through multiple pathways, categorizing its effects based on increased or decreased expression. Furthermore, it reviews drugs that alleviate NAFLD by modulating RBPs, aiming to offer valuable insights for drug-targeted therapies based on RBP regulatory networks.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Changjin Li, Fan Yang, Zuohui Yuan, Xiaoguo Wei

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









