The immunotherapy breakthroughs in cervical cancer: Focus on potential biomarkers and further therapy advances
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12597Keywords:
Cervical cancer, CC, immunotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICIs, biomarkersAbstract
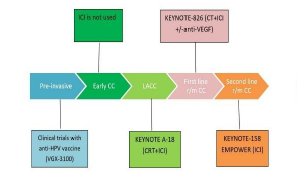
Despite the well-established role of human papillomavirus (HPV) as the primary cause of cervical cancer (CC) and the existence of an effective HPV vaccine, over half a million women are diagnosed with CC globally each year, with more than half of them dying from the disease. Immunotherapy has rapidly become a cornerstone of cancer treatment, offering substantial improvements in survival rates and reducing treatment-related side effects compared to traditional therapies. For the past 25 years, chemoradiotherapy (CRT) has been the standard treatment for locally advanced CC (LACC). However, while adjuvant chemotherapy has failed to improve outcomes in LACC, the integration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) with CRT, as well as chemoimmunoradiotherapy followed by consolidation immunotherapy, has transformed treatment strategies, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to CRT alone. In the first-line treatment of CC, adding pembrolizumab to platinum-based chemotherapy, either with or without bevacizumab, has significantly improved outcomes compared to platinum-based chemotherapy and bevacizumab alone. This review explores the current landscape of immunotherapy and biomarker advancements in CC. Furthermore, we discuss promising future directions, including the potential of personalized immunotherapy approaches and novel combination therapies to further enhance treatment efficacy and improve prognoses for patients with CC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maja Pezer Naletilić, Krešimir Tomić, Kristina Katić, Zoran Gatalica, Gordan Srkalović, Eduard Vrdoljak, Semir Vranić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









