Induced sputum KL-6 combined with HRCT scoring for diagnosing and monitoring idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12667Keywords:
Diagnosis, high-resolution computed tomography score, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, induced sputum, Krebs von den Lungen-6Abstract
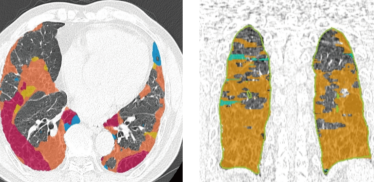
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and fatal interstitial lung disease for which reliable early diagnostic biomarkers are still lacking. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and monitoring value of induced sputum Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) levels in patients with IPF and to investigate their relationship with pulmonary function parameters and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scoring. In this prospective observational study, 20 patients with IPF and 20 age-matched healthy subjects (HS) were enrolled between October 2021 and April 2023. Induced sputum samples were collected for KL-6 measurement using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, while all participants underwent pulmonary function testing and HRCT scoring. KL-6 levels were significantly higher in the IPF group compared with the HS group [776.29 (interquartile range, IQR: 681.98–858.57) vs. 322.21 (IQR: 253.67–338.64) U/mL, p<0.001]. In IPF patients, induced sputum KL-6 levels showed strong negative correlations with multiple lung function indices, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) (all p<0.05), and a strong positive correlation with HRCT scores (r=0.908, p<0.001). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis demonstrated that combining KL-6 levels with HRCT scores yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.936 (95% confidence interval, CI: 0.914–0.944), with specificity of 97.5% and sensitivity of 80.0%. In conclusion, induced sputum KL-6 levels reflect the degree of pulmonary fibrosis and are closely associated with functional and imaging indicators in IPF. The combination of KL-6 with HRCT scoring enhances diagnostic accuracy, underscoring its potential clinical utility as a noninvasive biomarker for early detection and monitoring of IPF.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bingxin Zhang, Dejun Zhao, Danping Hu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









