Circulating microRNAs in prostate cancer — Non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and therapy: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12971Keywords:
Prostate cancer, miRNA, biomarkers, diagnosis, therapy, tumor microenvironmentAbstract
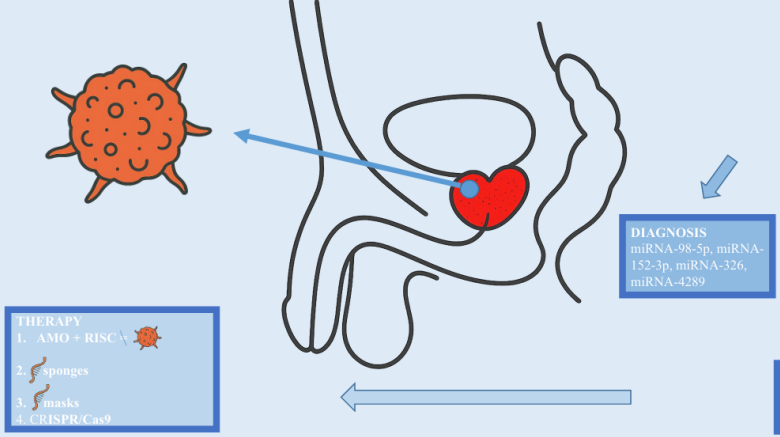
Prostate cancer (PC) is a common malignancy driven by interacting genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, including hereditary mutations (BRCA1/2, HPC1, AR variants), premalignant lesions [proliferative inflammatory atrophy (PIA), prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN)], and Western dietary patterns. This narrative review aims to synthesize evidence on the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in PC pathogenesis and clinical management across diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, and recurrence prediction. We searched PubMed/MEDLINE (2004–present) using predefined terms, screened reference lists, excluded outdated records, and prioritized biomarker studies with AUC ≥ 0.85. Current diagnostic pathways—digital rectal examination, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, multiparametric MRI, and Gleason-based International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading—are complemented by molecular tools (4Kscore, PHI, SelectMDx, TMPRSS2–ERG, PCA3, ConfirmMDx). MiRNAs, key post-transcriptional regulators, contribute to PC via dysregulated biogenesis and modulation of androgen receptor signaling within an inflamed, remodeled tumor microenvironment. Circulating and exosomal miRNAs (notably miR-21, miR-375, and miR-182-5p) exhibit greater specificity and stability than PSA, enabling non-invasive diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment monitoring, and recurrence prediction. Therapeutic approaches—antagomirs, sponges, miRNA masks, and CRISPR editing—show preclinical promise, while chemical modifications [peptide nucleic acids (PNAs), locked nucleic acids (LNAs), C2′ modifications] improve stability and delivery but remain limited by biodistribution, tissue penetration, off-target effects, and immunogenicity. In conclusion, standardized workflows and multicenter validation, integrated with clinical and imaging data, are essential to translate miRNA-based tools into precision PC management.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ema Volar, Borna Vuković, Ivan Franin, Zrinka Madunić, Anita Bijelić, Ivana Čelap, Nino Sinčić, Igor Tomašković, Jure Murgić, Monika Ulamec

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









