Multidrug resistance, diagnostic challenges, and treatment gaps in Pandoraea infections: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13126Keywords:
Pandoraea spp, multidrug-resistant pathogens, bacteriophages, antimicrobial peptides, combination antibiotic therapiesAbstract
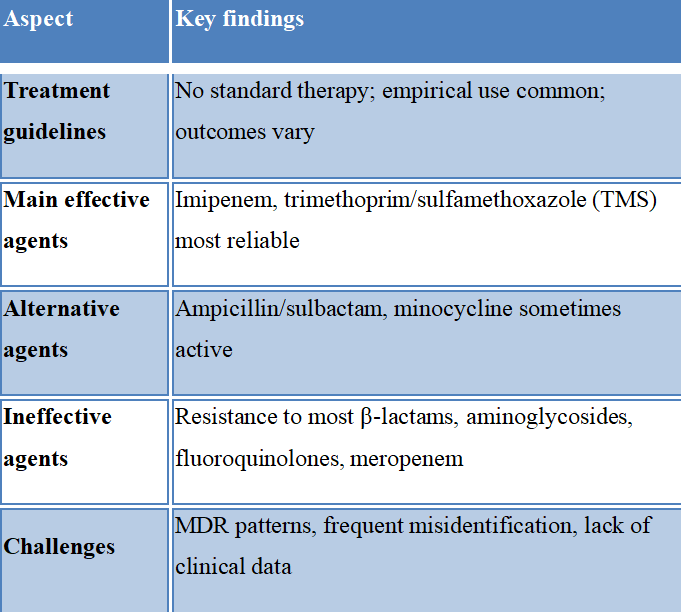
Pandoraea species are emerging multidrug-resistant pathogens increasingly associated with respiratory tract infections, particularly in cystic fibrosis patients. Despite their growing clinical relevance, these bacteria are underrepresented in the scientific literature. This review aims to consolidate existing evidence regarding Pandoraea species as emerging multidrug-resistant pathogens, with a focus on their taxonomy, diagnostic methodologies, antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, and treatment challenges. By identifying gaps in current therapeutic strategies and the limited clinical outcome data, this review underscores the necessity of advancing research into innovative interventions, such as bacteriophages, antimicrobial peptides, and combination therapies, to enhance patient management and infection control. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar, employing relevant keywords to identify case reports, clinical studies, and in vitro research related to Pandoraea infections, resistance mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. Our findings reveal a significant lack of comprehensive data on therapeutic approaches, particularly concerning bacteriophages, antimicrobial peptides, and combination antibiotic therapies. Furthermore, clinical data on treatment efficacy remain sparse, with the majority of evidence stemming from in vitro studies rather than real-world clinical settings. This review emphasizes the urgent need for further research to address these knowledge deficits and to develop effective therapeutic interventions against Pandoraea infections.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Waiel S. Halabi, Sulaiman Bani Abdel-Rahman, Hala Altarawneh, Rawan Altalhi, Loui A. Ismaeel, Khulud A. Alhazmi, Ohood S. Alharbi, Malaz Gazzaz, Sarah Almuhayya, Turki M. Alharthi, Bandar Hasan Saleh, Nabeel Hussain Alhussainy, Abdulaziz Alsaedi, Hatoon A. Niyazi, Hanouf A. Niyazi, Noha A. Juma, Mona Abdulrahman, Karem Ibrahem

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









