Investigation of in-vitro susceptibility of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from clinical specimens to tigecycline
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2013.2338Keywords:
tigecycline, Acinetobacter, Microdilution, Disk diffusion, E-testAbstract
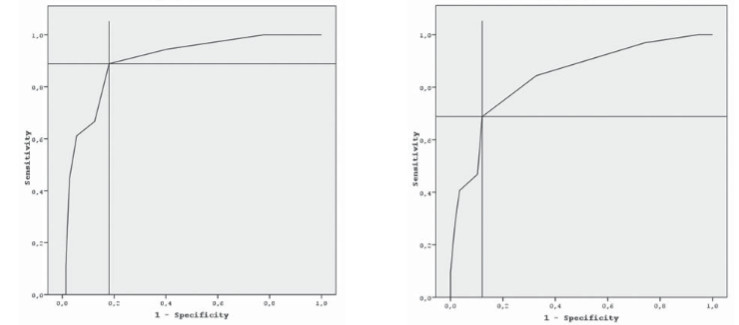
The management of infections due to A. baumannii is difficult because of rapidly developing resistance, however, tigecycline, a glycylcycline antimicrobial, is in use for several years. In the present study, it was aimed to determine the susceptibility rates of A. baumannii to tigecycline. A total of 90 A. baumanniisolates were tested using three methods such as disk diffusion, broth microdilution, and E-test. The MIC50and MIC90 values and the MIC range were found as 2 μg/ml, 4 μg/ml, and 0.1-8 μg/ml by microdilution; and 2 μg/ml, 6 μg/ml, and 0.1-12 μg/ml by E-test, respectively. There were a few major errors as well as the minor rates were all high as between 35.7%-46.7%. The accuracy rates between the methods were low as 53.3% (48/90) between disk diffusion and E-test, 51.1% (46/90) between disk diffusion and microdilution, and 60.0% (54/90) between E-test and microdilution. In the ROC curve analysis, an inhibition zone diameter of susceptibility breakpoint of 21.5 mm had sensitivity between 68.8%-88.9%; specificity between 81.9%-87.9%; and accuracy between 80.0%-83.33%. An analysis based on EUCAST’s non-species breakpoints, the MIC tests showed higher accuracy with a rate of 96.7%, however, performance of disk diffusion got worse as lower than 25%. In conclusion, we showed that the reliability of the methods even did not remain as high as the past. Our study presented that none of three methods revealed reliable results in determination of susceptibility of A. baumanni to tigecycline, so the clinical response should be followed up carefully in such cases.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-08-08
Published 2013-11-20









