Outcomes of 3% Green Tea Emulsion on Skin Sebum Production in Male Volunteers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2010.2697Keywords:
Camellia sinensis L, ANOVA, skin sebum, Abil’EM90, formulationAbstract
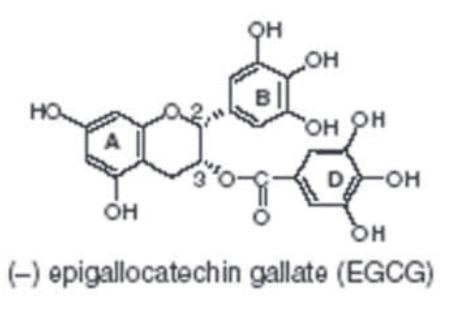
This study was aimed to depict potential effects of stable formulation (water in oil emulsion), containing 3% green tea (Camellia sinensis L) extract on skin sebum production in healthy human volunteers.
For this purpose formulation was designed using 3 % ethanolic green tea extract and Abil’EM90 was used as an emulsifier. Formulation was applied to the cheeks of healthy human volunteers (n=10) for a period of 8 weeks. Measurements for skin sebum production were considered using Sebumeter MPA 5. Results were compiled and any effect produced by the formulation was justified statistically. It was observable that statistically significant (p < 0.5 %) results were found for skin sebum production after long term application of the formulation. 3% formulation of green tea extract was ideal in all aspects and can be experienced in skin disorders like acne to further investigate its effects in unhealthy volunteers.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-11-22
Published 2010-08-20









