Surveillance of Intrahospital Infections at the Clinic for Gynaecology and Obstetrics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2009.2859Keywords:
intrahospital infections, antibiotics resistance, surveillanceAbstract
Intrahospital infections (IHI) and antibiotics resistance are the problems which exist in virtually all hospitals in the world.
The main aim of the present research is establishing of epidemiological surveillance over occurrence of IHI at the Clinic for Gynaecology and Obstetrics at the University Clinical Center Tuzla and thus identifies: types of bacteria which cause IHI, types of infection according to anatomical localization and research resistance organisms causing of IHI on antimicrobial drugs. A study was implemented on all patients admitted to Clinic for Gynaecology and Obstetrics during the period of one year and who subsequently developed infection. Determination of intrahospital infections was done according to criteria defined by the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention from the United States.
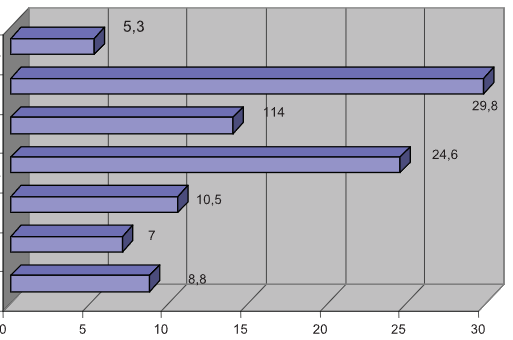
The results of our work have shown that both urinary tract infections and surgical site infections are the most frequent. As IHI causers the most found are gram-negative organisms (73,7%), such as Escherichia coli (29,8%), right after that Klebsiella pneumoniae (24,6%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (14%) and Proteus mirabilis (5,3%) (p<0,05). Gram-positive organisms as causers of IHI are registered in 26,3% cases. Out of that Streptococcus species are isolated in 10,5% cases, Staphylococcus aureus (8,8%) and coagulasa negative staphylococci (7%) (p>0,05). High percent resistance of bacteria was evident to beta-lactams, aminoglycosids and cephalosporin’s of third generation. Gram-positive organisms were 100% sensitive to vancomycin, while gram-negative organisms manifested the high percent of sensibility to imipenem and cefepime.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-12-19
Published 2009-02-20









