Serum extracellular vesicle microRNA dysregulation and childhood trauma in adolescents with major depressive disorder
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7110Keywords:
Extracellular vesicle, miRNA, childhood trauma, major depressive disorder, adolescentAbstract
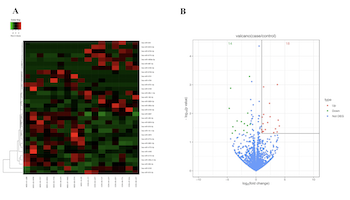
Major depressive disorder (MDD) seriously endangers adolescent mental and physical health. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are mediators of cellular communication and are involved in many physiological brain processes. Although EV miRNAshave been implicated in adults with major psychiatric disorders, investigation into their effects in adolescent MDDremains scarce. In discovery set, we conducted a genome-wide miRNA sequencing of serum EVs from 9 untreated adolescents with MDD and 8 matched healthy controls (HCs), identifying 32 differentially expressed miRNAs (18 upregulated and 14 downregulated). In the validation set, 8 differentially expressed and highly enriched miRNAs were verified in independent samples using RT-PCR, with 4 (miR-450a-2-3p, miR-3691-5p, miR-556-3p, and miR-2115-3p) of the 8 miRNAs found to be significantly elevated in 34 untreated adolescents with MDD compared with 38 HCs and consistent with the sequencing results. After the Bonferroni correction, we found that three miRNAs (miR-450a-2-3p, miR-556-3p, and miR-2115-3p) were still significantly different. Among them, miR-450a-2-3p showed the most markeddifferential expression and was able to diagnose disease with 67.6% sensitivity and 84.2% specificity. Furthermore, miR-450a-2-3p partially mediated the associations between total childhood trauma, emotional abuse, and physical neglect and adolescent MDD. We also found that the combination of miR-450a-2-3p and emotional abuse could effectively diagnose MDD in adolescents with 82.4% sensitivity and 81.6% specificity. Our data demonstrate the association of serum EV miRNA dysregulation with MDD pathophysiology and, furthermore, show that miRNAs may mediate the relationship between early stress and MDD susceptibility. We also provide a valid integrated model for the diagnosis of adolescent MDD.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Liu-yi Ran, Yi-ting Kong, Jiao-jiao Xiang, Qi Zeng, Chen-yu Zhang, Lei Shi, Hai-tang Qiu, Chuan Liu, Lin-li Wu, Ya-lan Li, Jian-mei Chen, Ming Ai, Wo Wang, Li Kuang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-05-23
Published 2022-10-23









