Jun-APOE-LRP1 axis promotes tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9248Keywords:
Apolipoproteins, colorectal cancer (CRC), transcription factor, lipoprotein receptor (LRP), metastasisAbstract
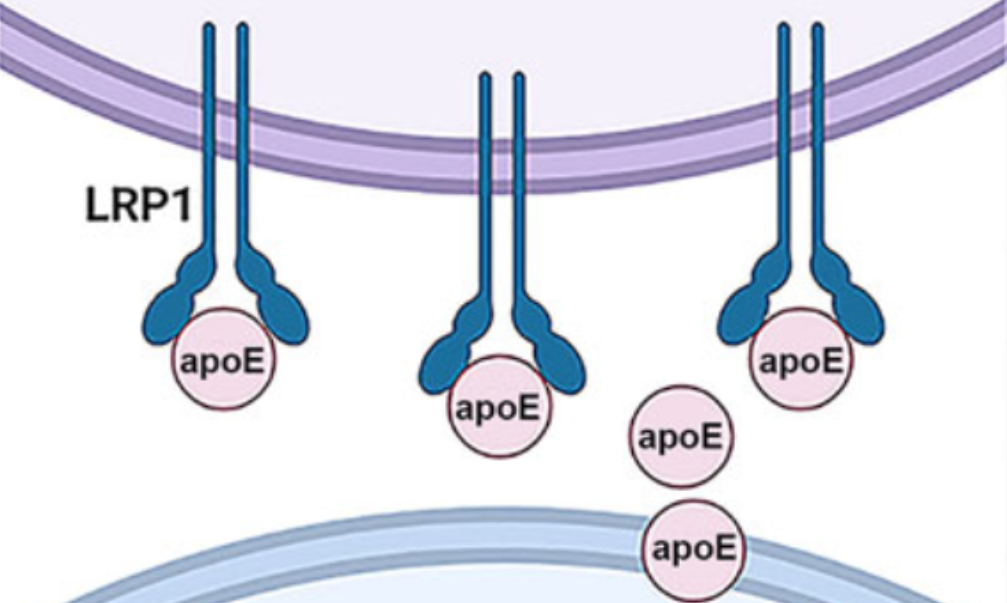
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) has previously been reported to play vital roles in tumor progression. However, the impact of apoE on colorectal cancer (CRC) metastasis remains largely unexplored. This study aimed to investigate the role of apoE in CRC metastasis and to identify the transcription factor and receptor of apoE involved in regulation of CRC metastasis. Bioinformatic analyses were conducted to examine the expression pattern and prognosis of apolipoproteins. APOE-overexpressing cell lines were utilized to explore the effects of apoE on proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells. Additionally, the transcription factor and receptor of apoE were screened via bioinformatics, and further validated through knockdown experiments. We discovered that the mRNA levels of APOC1, APOC2, APOD and APOE were higher in lymphatic invasion group, and a higher apoE level indicated poorer overall survival and progression-free interval. In vitro studies demonstrated that APOE-overexpression did not affect proliferation but promoted the migration and invasion of CRC cells. We also reported that APOE-expression was modulated by the transcription factor Jun by activating the proximal promoter region of APOE, and APOE-overexpression reversed the metastasis suppression of JUN knockdown. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis suggested an interaction between apoE and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1). LRP1 was highly expressed in both the lymphatic invasion group and the APOEHigh group. Additionally, we found that APOE-overexpression upregulated LRP1 protein levels, and LRP1 knockdown attenuated the metastasis-promoting function of APOE. Overall, our study suggests that the Jun-APOE-LRP1 axis contributes to tumor metastasis in CRC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Lingyuan He, Mengchen Shi, Shuwei Ren, Jingdan Zhang, Yu Tian, Xiangling Yang, Huanliang Liu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-06-03
Published 2023-11-03









