Gaining consensus on expert rule statements for acute respiratory failure digital twin patient model in intensive care unit using a Delphi method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9344Keywords:
Digital twin, intensive care unit, respiratory failure, hypoxia, concensus, critical care, DelphiAbstract
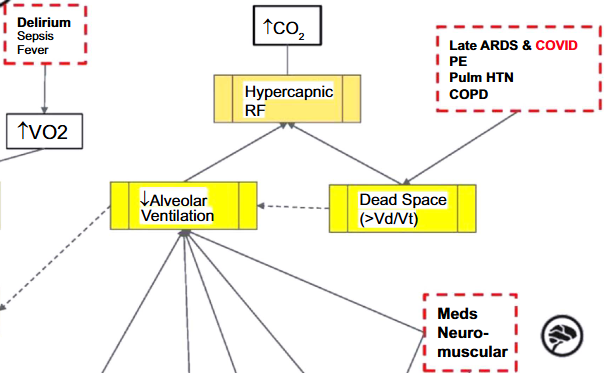
Digital twin technology is a virtual depiction of a physical product and has been utilized in many fields. Digital twin patient model in healthcare is a virtual patient that provides opportunities to test the outcomes of various interventions virtually without subjecting an actual patient to possible harm. This can serve as a decision aid in the complex environment of the intensive care unit (ICU). Our objective is to develop consensus among a multidisciplinary expert panel on statements regarding respiratory pathophysiology contributing to respiratory failure in the medical ICU. We convened a panel of 34 international critical care experts. Our group modeled elements of respiratory failure pathophysiology using directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) and derived expert statements describing associated ICU clinical practices. The experts participated in three rounds of modified Delphi to gauge agreement on 78 final questions (13 statements with 6 substatements for each) using a Likert scale. A modified Delphi process achieved agreement for 62 of the final expert rule statements. Statements with the highest degree of agreement included the physiology, and management of airway obstruction decreasing alveolar ventilation and ventilation-perfusion matching. The lowest agreement statements involved the relationship between shock and hypoxemic respiratory failure due to heightened oxygen consumption and dead space. Our study proves the utility of a modified Delphi method to generate consensus to create expert rule statements for further development of a digital twin-patient model with acute respiratory failure. A substantial majority of expert rule statements used in the digital twin design align with expert knowledge of respiratory failure in critically ill patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Amy J. Montgomery, John Litell, Johnny Dang, Laure Flurin, Ognjen Gajic, Amos Lal, on behalf of Digital Twin Platform for education, research, and healthcare delivery investigator group

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-06-29
Published 2023-11-03









