Exosome miR-4738-3p-mediated regulation of COL1A2 through the NF-κB and inflammation signaling pathway alleviates osteoarthritis low-grade inflammation symptoms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9921Keywords:
Exosome, microRNA (miR)-4739-3p, collagen type I alpha 2 chain (COL1A2), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, osteoarthritis (OA)Abstract
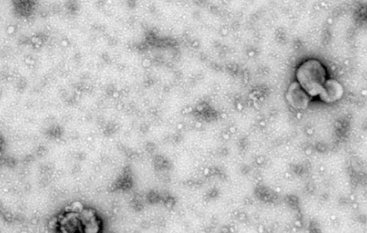
This study aimed to elucidate the roles of microRNA (miR)-4738-3p and the collagen type I alpha 2 chain (COL1A2) gene in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) through bioinformatics analysis and cellular assays. The GSE55235 dataset was analyzed using the weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) method to identify gene modules associated with OA. Key overlapping genes were identified from these modules and the GSE55235-differential expressed genes (DEGs). The expression levels of selected genes were determined in C28/I2 cells using the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The interaction between miR-4738-3p and COL1A2 was examined in the context of interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) induction. Exosome characterization was achieved through transmission electron microscopy (TEM), western blotting (WB), and other analyses. The study also investigated the functional relevance of miR-4738-3p in OA pathology through various molecular and cellular assays. Our findings revealed that the green module exhibited a strong correlation with the OA phenotype in the GSE55235 dataset, with COL1A2 emerging as a hub gene and miR-4738-3p as its key downstream target. IL-1β induction suggested that COL1A2 is involved in inflammation and apoptosis, while miR-4738-3p appeared to play an antagonistic role. The analysis of exosomes underscored the significance of miR-4738-3p in cellular communication, with an enhanced level of exo-miR-4738-3p antagonizing IL-1β-induced inflammation and promoting cell survival. Conversely, a reduction in exo-miR-4738-3p led to increased cell damage. This study established a clear regulatory relationship between miR-4738-3p and COL1A2, with the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway playing a central role in this regulation. The miR-4738-3p significantly influences the OA-associated inflammation, primarily through modulation of COL1A2 and the NF-κB pathway. Therefore, targeting miR-4738-3p offers a potential therapeutic approach for OA, with exosome miR-4738-3p presenting a promising strategy.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jun Xu, Kaifeng Zhou, Huijie Gu, Yiming Zhang, Liang Wu, Chong Bian, Zhongyue Huang, Guangnan Chen, Xiangyang Cheng, Xiaofan Yin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-11-21
Published 2024-05-02









