ALKBH5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating TTI1 expression
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10247Keywords:
Liver hepatocellular carcinoma, ALKBH5, TTI1, proliferation, migration, invasionAbstract
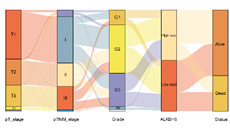
The objective of this research was to investigate the potential mechanisms of AlkB homolog 5, RNA demethylase (ALKBH5) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We used The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Kruskal-Wallis method and Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival analysis to study the expression of ALKBH5 and its correlation with clinical factors in HCC. In vitro experiments verified the expression of ALKBH5 and its effect on HCC cell phenotype. We screened differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from HCC patients associated with ALKBH5. Through this screening we identified the downstream gene TTI1 which is associated with ALKBH5 and investigated its function using Gene Expression Profiling Interaction Analysis (GEPIA) along with univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. Finally, we analyzed the functions of ALKBH5 and TTI1 in HCC cells. Across numerous pan-cancer types, we observed significant overexpression of ALKBH5. In vitro experiments confirmed ALKBH5 as an oncogene in HCC, with its knockdown leading to suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Bioinformatics analyses also demonstrated a significant positive correlation between ALKBH5 and TTI1. TTI1, highly expressed in cells, showed promising prognostic ability for patients. Further experiments confirmed that suppressing TTI1 impeded cell growth and movement, with this effect partially offset by increased ALKBH5 expression. Conversely, promoting these cellular processes was observed with TTI1 overexpression, but was dampened by decreased ALKBH5 expression. In conclusion, our findings suggest that ALKBH5 may influence proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC by modulating TTI1 expression, providing a new direction for treating HCC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Qimeng Chang, Xiang Zhou, Huarong Mao, Jinfeng Feng, Xubo Wu, Ziping Zhang, Zhiqiu Hu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









