Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on liver fat content: A meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12203Keywords:
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2, SGLT2, liver fat content, LFC, type 2 diabetes, T2DMAbstract
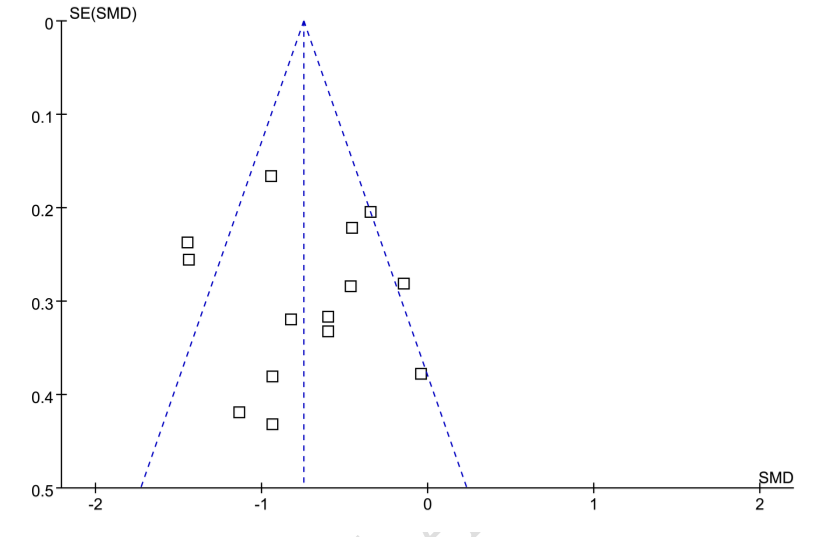
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a major metabolic disorder linked to increased morbidity and mortality. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, commonly used to manage type 2 diabetes (T2DM), have shown potential in reducing liver fat content (LFC). However, the magnitude and consistency of this effect remain uncertain. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on LFC in adults with metabolic disorders. A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science was conducted up to January 2, 2024, to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on LFC. Studies were included if they reported liver fat changes measured by magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) or proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (¹H-MRS). We pooled standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using a random-effects model to account for variability across studies. Thirteen RCTs with 14 datasets (n = 791 participants) were included. SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced LFC compared to controls (SMD: −0.73, 95% CI: −0.97 to −0.50; P < 0.001), with moderate heterogeneity (I² = 62%). Subgroup and meta-regression analyses did not identify any study characteristics—such as study design, diabetic status, patient demographics, baseline LFC, type of SGLT2 inhibitor, or treatment duration—as significant contributors to heterogeneity (all P > 0.05). In conclusion, SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with a significant reduction in LFC in adults, supporting their potential role in managing MASLD.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Quanli Ge, Fengling Zhang, Yong Liu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









