Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating microRNA-21 in heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13164Keywords:
Circulating miRNA, micro-RNA, miRNA-21, heart failure, diagnostic valueAbstract
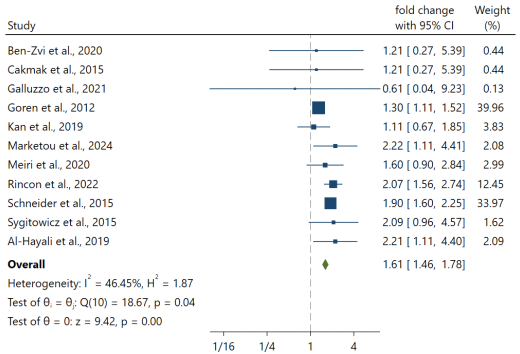
Heart failure (HF) remains a leading cause of global mortality, underscoring the urgent need for reliable, minimally invasive biomarkers to facilitate early diagnosis and risk stratification. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) has been implicated in cardiac fibrosis, hypertrophy, and the progression of HF; however, its clinical utility remains uncertain. This study presents a systematic review and diagnostic test accuracy (DTA) meta-analysis aimed at assessing the diagnostic and prognostic performance of circulating miR-21 in HF. We estimated pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) for the DTA analysis, and synthesized hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for prognostic outcomes. Additionally, univariate meta-regression was conducted to explore demographic and clinical moderators. Our analysis included fourteen studies with a total of 1,327 participants. Results demonstrated that circulating miR-21 levels were significantly elevated in HF patients compared to controls (fold change 1.61; 95% CI 1.46–1.78; p < 0.001). The diagnostic accuracy was notably high, with a sensitivity of 0.94 (95% CI 82.0–98.0), specificity of 0.90 (95% CI 79.0–96.0), and AUC of 0.97 (95% CI 96.0–98.0). Elevated levels of miR-21 were associated with an increased risk of worsening HF severity (HR 1.84; 95% CI 1.14–2.97; p=0.01) and HF-related cardiovascular death (HR 2.00; 95% CI 1.30–3.03; p=0.001). However, no significant association was found with HF-related hospitalization (HR 0.97; 95% CI 0.61–1.52; p=0.88). Variability in sample type and differing clinical thresholds contributed to heterogeneity across studies. These findings support the potential of circulating miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for HF. Nevertheless, further research with standardized sample sizes and clinical thresholds is necessary to establish robust evidence for its clinical application.
Citations
Downloads
References
Khan MS, Shahid I, Bennis A, Rakisheva A, Metra M, Butler J. Global epidemiology of heart failure. Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2024;21(10):717–34.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-024-01046-6
Melman YF, Shah R, Das S. MicroRNAs in Heart Failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2014;7(1):203–14.
https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000266
Gaggin HK, Januzzi JL. Biomarkers and diagnostics in heart failure. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2013;1832(12):2442–50.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.12.014
Rincón LM, Rodríguez‐Serrano M, Conde E, Lanza VF, Sanmartín M, González‐Portilla P, et al. Serum microRNAs are key predictors of long‐term heart failure and cardiovascular death after myocardial infarction. ESC Heart Fail. 2022;9(5):3367–79.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.13919
Bartel DP. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell. 2018;173(1):20–51.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.006
Cordes KR, Srivastava D. MicroRNA Regulation of Cardiovascular Development. Circ Res. 2009;104(6):724–32.
https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.192872
Olivieri F, Spazzafumo L, Bonafè M, Recchioni R, Prattichizzo F, Marcheselli F, et al. MiR-21-5p and miR-126a-3p levels in plasma and circulating angiogenic cells: relationship with type 2 diabetes complications. Oncotarget. 2015;6(34):35372–82.
https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6164
Scrutinio D, Conserva F, Passantino A, Iacoviello M, Lagioia R, Gesualdo L. Circulating microRNA-150-5p as a novel biomarker for advanced heart failure: A genome-wide prospective study. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2017;36(6):616–24.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2017.02.008
Xue R, Tan W, Wu Y, Dong B, Xie Z, Huang P, et al. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Heart Failure. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.592412
Qiao L, Hu S, Liu S, Zhang H, Ma H, Huang K, et al. microRNA-21-5p dysregulation in exosomes derived from heart failure patients impairs regenerative potential. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2019;129(6):2237–50.
https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI123135
Bang C, Batkai S, Dangwal S, Gupta SK, Foinquinos A, Holzmann A, et al. Cardiac fibroblast-derived microRNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2014;124(5):2136–46.
https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI70577
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):89.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529–36.
https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
Lin L, Chu H. Quantifying Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics. 2018;74(3):785–94.
https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12817
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(9):882–93.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.01.016
Al-Hayali MA, Sozer V, Durmus S, Erdenen F, Altunoglu E, Gelisgen R, et al. Clinical Value of Circulating Microribonucleic Acids miR-1 and miR-21 in Evaluating the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure in Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Biomolecules. 2019;9(5):193.
https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050193
Ben‐Zvi I, Volinsky N, Grosman‐Rimon L, Haviv I, Rozen G, Andria N, et al. Cardiac‐peripheral transvenous gradients of microRNA expression in systolic heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2020;7(3):835–43.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12597
Cakmak HA, Coskunpinar E, Ikitimur B, Barman HA, Karadag B, Tiryakioglu NO, et al. The prognostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure. Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. 2015;16(6):431–7.
https://doi.org/10.2459/JCM.0000000000000233
Davydova V, Bezhanishvili TG, Filatova ME, Andreeva SE, Streltsova AA, Poliakova AA, et al. Expression of miRNA-21 level in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients with chronic heart failure and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: results of a 6-year follow-up. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(Supplement_2).
https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/ehaa946.2088
Galluzzo A, Gallo S, Pardini B, Birolo G, Fariselli P, Boretto P, et al. Identification of novel circulating microRNAs in advanced heart failure by next‐generation sequencing. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8(4):2907–19.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.13371
Goren Y, Kushnir M, Zafrir B, Tabak S, Lewis BS, Amir O. Serum levels of microRNAs in patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(2):147–54.
https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfr155
Kan C, Cao J, Hou J, Jing X, Zhu Y, Zhang J, et al. Correlation of miR-21 and BNP with pregnancy-induced hypertension complicated with heart failure and the diagnostic value. Exp Ther Med. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7286
Marketou M, Kontaraki J, Zacharis E, Maragkoudakis S, Fragkiadakis K, Kampanieris E, et al. Peripheral Blood MicroRNA-21 as a Predictive Biomarker for Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Old Hypertensives. Am J Hypertens. 2024;37(4):298–305.
https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpad109
Meiri E, Volinsky N, Dromi N, Kredo‐Russo S, Benjamin H, Tabak S, et al. Differential expression of microRNA in serum fractions and association of Argonaute 1 microRNAs with heart failure. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(12):6586–95.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15306
Schneider S, Silvello D, Martinelli N, Garbin A, Biolo A, Clausell N, et al. Plasma levels of microRNA-21, -126 and -423-5p alter during clinical improvement and are associated with the prognosis of acute heart failure. Mol Med Rep. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.8428
Zhang J, Xing Q, Zhou X, Li J, Li Y, Zhang L, et al. Circulating miRNA-21 is a promising biomarker for heart failure. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):7766–74.
https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7575
Sygitowicz G, Tomaniak M, Błaszczyk O, Kołtowski Ł, Filipiak KJ, Sitkiewicz D. Circulating microribonucleic acids miR-1, miR-21 and miR-208a in patients with symptomatic heart failure: Preliminary results. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;108(12):634–42.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2015.07.003
Ding H, Wang Y, Hu L, Xue S, Wang Y, Zhang L, et al. Combined detection of miR-21-5p, miR-30a-3p, miR-30a-5p, miR-155-5p, miR-216a and miR-217 for screening of early heart failure diseases. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(3).
https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20191653
Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T, Kissler S, Bussen M, et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature. 2008;456(7224):980–4.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07511
Yan M, Chen C, Gong W, Yin Z, Zhou L, Chaugai S, et al. miR-21-3p regulates cardiac hypertrophic response by targeting histone deacetylase-8. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;105(3):340–52.
https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu254
Pan ZW, Lu YJ, Yang BF. MicroRNAs: a novel class of potential therapeutic targets for cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31(1):1–9.
https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.175
Guo R, Nair S. Role of microRNA in diabetic cardiomyopathy: From mechanism to intervention. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2017;1863(8):2070–7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.03.013
Wong LL, Armugam A, Sepramaniam S, Karolina DS, Lim KY, Lim JY, et al. Circulating microRNAs in heart failure with reduced and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(4):393–404.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.223
Holland A, Enrick M, Diaz A, Yin L. Is miR-21 A Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease? International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology. 2023:26–36.
https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.0201003
Chrysohoou C, Konstantinou K, Tsioufis K. The Role of NT-proBNP Levels in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction-It Is Not Always a Hide-and-Seek Game. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024;11(7):225.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd11070225
Cheng Y, Zhao W, Zhang X, Sun L, Yang H, Wang Y, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-1 attenuates glucose-induced apoptosis by regulating the liver X receptor α in cardiomyocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):1814–24.
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6388
Kura B, Kalocayova B, Devaux Y, Bartekova M. Potential Clinical Implications of miR-1 and miR-21 in Heart Disease and Cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):700.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030700
Yang J, Yang XS, Fan SW, Zhao XY, Li C, Zhao ZY, et al. Prognostic value of microRNAs in heart failure. Medicine. 2021;100(46):e27744.
https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000027744
Dai B, Wang F, Nie X, Du H, Zhao Y, Yin Z, et al. The Cell Type-Specific Functions of miR-21 in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Genet. 2020;11.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Annisa Salsabilla Dwi Nugrahani, Wynne Widiarti, Roy Novri Ramadhan, Citrawati Dyah Kencono Wungu, Hendri Susilo, Indah Mohd Amin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









