Gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease – Immunomodulatory mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic opportunities: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13213Keywords:
Gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles, Alzheimer’s disease, neuroinflammation, immune regulation, gut-brain axis, microbiota-immune-neuro axisAbstract
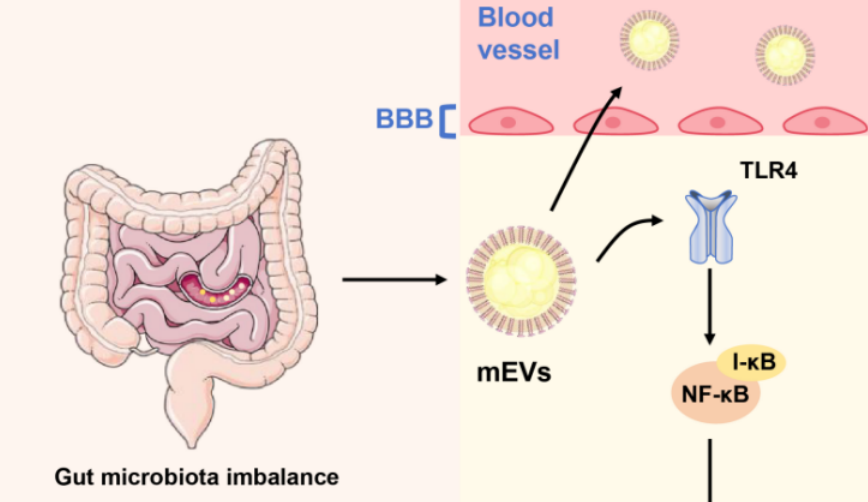
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that poses a growing global health challenge. Beyond traditional hallmarks such as amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition, tau hyperphosphorylation, and neuroinflammation, the gut–brain axis (GBA) has emerged as a significant modulator of AD pathogenesis. Among gut-derived mediators, microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles (mEVs) transport bioactive cargo across epithelial and vascular barriers, thereby linking intestinal dysbiosis to neurodegeneration. This narrative review synthesizes experimental, translational, and early clinical evidence regarding the immunomodulatory roles of gut mEVs in AD. We examine how mEVs may traverse compromised intestinal and blood–brain barriers, activate microglia and astrocytes, and influence Aβ and tau metabolism, thereby integrating peripheral and central immune interactions. Based on this evidence, we propose the "microbiota–EV–immune–neuro axis" as a conceptual framework that connects gut dysbiosis with AD-related neurodegeneration. The review also highlights emerging data on mEV signatures as minimally invasive biomarkers and explores their potential as therapeutic targets or delivery vectors. While current evidence is preliminary and methodologically heterogeneous, mEVs are increasingly recognized as both indicators and potential modulators of AD pathophysiology, emphasizing the need for standardized, longitudinal, and interventional studies.
Citations
Downloads
References
Ricci, C., Neurodegenerative disease: from molecular basis to therapy. MDPI, 2024. p. 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/books978-3-7258-0187-9
Chen, Y. and Y. Yu, Tau and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: interplay mechanisms and clinical translation. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 2023. 20(1): p. 165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-023-02853-3
Megur, A., et al., The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Alzheimer's Disease: Neuroinflammation Is to Blame? Nutrients, 2021. 13(1): p. 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010037
Doroszkiewicz, J., et al., Metabolic and immune system dysregulation: Unraveling the connections between Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, inflammatory bowel diseases, and rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2024. 13(17): p. 5057. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175057
Sehar, U., et al., Amyloid Beta in Aging and Alzheimer's Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022. 23(21): p. 12924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112924
Bloom, G.S., Amyloid-β and Tau: The Trigger and Bullet in Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. JAMA Neurology, 2014. 71(4): p. 505-508. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847
Leong, Y.Q., et al., Mechanisms of action of amyloid-beta and its precursor protein in neuronal cell death. Metabolic Brain Disease, 2020. 35(1): p. 11-30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00516-y
Kepp, K.P., et al., The amyloid cascade hypothesis: an updated critical review. Brain, 2023. 146(10): p. 3969-3990. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awad159
Crimins, J.L., et al., The intersection of amyloid beta and tau in glutamatergic synaptic dysfunction and collapse in Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Research Reviews, 2013. 12(3): p. 757-763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2013.03.002
Edwards, F.A., A unifying hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: from plaques to neurodegeneration. Trends in Neurosciences, 2019. 42(5): p. 310-322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2019.03.003
Kamat, P.K., et al., Mechanism of oxidative stress and synapse dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: understanding the therapeutics strategies. Molecular Neurobiology, 2016. 53(1): p. 648-661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9053-6
Tönnies, E. and E. Trushina, Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer's Disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2017. 57(4): p. 1105-1121. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-161088
Wang, W.Y., et al., Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Transl Med, 2015. 3(10): p. 136.
Cai, Z., M.D. Hussain, and L.-J. Yan, Microglia, neuroinflammation, and beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Neuroscience, 2014. 124(5): p. 307-321. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2013.833510
Thakur, S., et al., Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Progress in Molecular Signaling and Therapeutics. Inflammation, 2023. 46(1): p. 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01721-1
Xie, J., L. Van Hoecke, and R.E. Vandenbroucke, The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Alzheimer's Disease Pathology. Frontiers in Immunology, 2022. Volume 12 - 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.796867
Takeda, S., N. Sato, and R. Morishita, Systemic inflammation, blood-brain barrier vulnerability and cognitive/non-cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer disease: Relevance to pathogenesis and therapy. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2014. Volume 6 - 2014. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00171
Huang, X., B. Hussain, and J. Chang, Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2021. 27(1): p. 36-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13569
Sultan, S., Gut Microbiota Extracellular Vesicles as Signaling Carriers in Host-Microbiota Crosstalk. Université d'Ottawa/University of Ottawa, 2023.
Schwechheimer, C. and M.J. Kuehn, Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: biogenesis and functions. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015. 13(10): p. 605-619. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3525
Brown, L., et al., Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015. 13(10): p. 620-630. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3480
Melo-Marques, I., S.M. Cardoso, and N. Empadinhas, Bacterial extracellular vesicles at the interface of gut microbiota and immunity. Gut Microbes, 2024. 16(1): p. 2396494. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2024.2396494
Wang, S., et al., Extracellular vesicles: A crucial player in the intestinal microenvironment and beyond. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024. 25(6): p. 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063478
Cuesta, C.M., et al., Role of microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles in gut-brain communication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021. 22(8): p. 4235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084235
Marquez-Paradas, E., et al., Microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles: current knowledge, gaps, and challenges in precision nutrition. Frontiers in Immunology, 2025. 16: p. 1514726. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1514726
Kaisanlahti, A., et al., Bacterial extracellular vesicles-brain invaders? A systematic review. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 2023. 16: p. 1227655. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2023.1227655
Ramos-Zaldívar, H.M., et al., Extracellular vesicles through the blood-brain barrier: a review. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS, 2022. 19(1): p. 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12987-022-00359-3
Benameur, T., et al., Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Mediators of Gut-Brain Communication in Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101398
Xiang, A., Identifying the Roles of Circulating Factors and Extracellular Vesicles in the Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, 2024.
Kim, H.S., et al., Gram-negative bacteria and their lipopolysaccharides in Alzheimer's disease: pathologic roles and therapeutic implications. Translational Neurodegeneration, 2021. 10(1): p. 49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-021-00273-y
Sun, B., et al., Emerging therapeutic role of gut microbial extracellular vesicles in neurological disorders. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2023. 17: p. 1241418. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1241418
Parsi, S., miRNAs as therapeutic agents in neurodegeneration: a pilot study. 2016.
Najdaghi, S., et al., The role of extracellular vesicles and microparticles in central nervous system disorders: mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic potential. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 2024. 44(1): p. 82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-024-01518-w
Xia, Y., et al., Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles restore Th17/Treg homeostasis in periodontitis via miR-1246. The FASEB Journal, 2023. 37(11): p. e23226. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202300674RR
Díaz-Garrido, N., et al., Transcriptomic microRNA profiling of dendritic cells in response to gut microbiota-secreted vesicles. Cells, 2020. 9(6): p. 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061534
Tong, L., et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG derived extracellular vesicles modulate gut microbiota and attenuate inflammatory in DSS-induced colitis mice. Nutrients, 2021. 13(10): p. 3319. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103319
·Wei, S., et al., Alzheimer's Disease-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Exacerbate Cognitive Dysfunction, Modulate the Gut Microbiome, and Increase Neuroinflammation and Amyloid-β Production. Molecular Neurobiology, 2025. 62(4): p. 5109-5132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04579-6
Eberl, C., et al., Reproducible colonization of germ-free mice with the oligo-mouse-microbiota in different animal facilities. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020. 10: p. 2999. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02999
Mianoor, Z., Sex specific differences in Alzheimer's disease and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia plasma biomarkers in healthy individuals. 2024.
Su, H., et al., Characterization of brain-derived extracellular vesicle lipids in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2021. 10(7): p. e12089. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12089
Lin, K., et al., Plasma exosomal miRNA expression and gut microbiota dysbiosis are associated with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2025. 19: p. 1545690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2025.1545690
Canseco-Rodriguez, A., et al., Long Non-Coding RNAs, Extracellular Vesicles and Inflammation in Alzheimer's Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022. 23(21): p. 13171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113171
André, P., et al., Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, soluble CD14, and the long-term risk of Alzheimer's disease: a nested case-control pilot study of older community dwellers from the three-city cohort. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2019. 71(3): p. 751-761. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-190295
Ismael, R., From Gut to Brain: Exploring the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Multiple Sclerosis. 2024.
Su, K.-Y., et al., Bacterial extracellular vesicles in biofluids as potential diagnostic biomarkers. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 2022. 22(12): p. 1057-1062. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2022.2166403
Jain, H., et al., Characterisation of LPS+ bacterial extracellular vesicles along the gut‐hepatic portal vein‐liver axis. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2024. 13(7): p. e12474. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12474
Pham, L.H.P., et al., Assessing Alzheimer's disease via plasma extracellular vesicle-derived mRNA. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, 2024. 16(3): p. e70006. https://doi.org/10.1002/dad2.70006
Taha, H.B., Extracellular vesicles for Alzheimer's disease and dementia diagnosis. medRxiv, 2024: p. 2024.04.24.24306155. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.24.24306155
Torrini, F., et al., Monitoring neurodegeneration through brain-derived extracellular vesicles in biofluids. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2025.03.006
Zhao, X., et al., Gut‐derived bacterial vesicles carrying lipopolysaccharide promote microglia‐mediated synaptic pruning. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2025. 21(8): p. e70331. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.70331
Li, X., et al., Extracellular vesicle-based point-of-care testing for diagnosis and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2025. 11(1): p. 65. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00916-4
Choi, D. and E.-Y. Lee, Standardizing Bacterial Extracellular Vesicle Purification: A Call for Consensus. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2025. 35: p. e2506011. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2506.06011
De Langhe, N., et al., Mapping bacterial extracellular vesicle research: insights, best practices and knowledge gaps. Nature Communications, 2024. 15(1): p. 9410. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53279-1
Kim, N.Y., et al., Effect of gut microbiota-derived metabolites and extracellular vesicles on neurodegenerative disease in a gut-brain axis chip. Nano Convergence, 2024. 11(1): p. 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-024-00413-w
Fonseca, S., et al., Extracellular vesicles produced by the human gut commensal bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron elicit anti-inflammatory responses from innate immune cells. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022. Volume 13 - 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1050271
Zhang, X., et al., The biological activity and potential of probiotics-derived extracellular vesicles as postbiotics in modulating microbiota-host communication. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2025. 23(1): p. 349. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-025-03435-6
Zhang, C., et al., Engineered Extracellular Vesicle-Based Nanoformulations That Coordinate Neuroinflammation and Immune Homeostasis, Enhancing Parkinson's Disease Therapy. ACS Nano, 2024. 18(34): p. 23014-23031. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c04674
Liang, X., et al., Engineering of extracellular vesicles for efficient intracellular delivery of multimodal therapeutics including genome editors. Nature Communications, 2025. 16(1): p. 4028.
Ghosh, M., A.-H. Bayat, and D.D. Pearse, Small Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Disease: Emerging Roles in Pathogenesis, Biomarker Discovery, and Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025. 26(15): p. 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157246
Du, X., et al., Bifidobacterium lactis-derived vesicles attenuate hippocampal neuroinflammation by targeting IL-33 to regulate FoxO6/P53 signaling. Nutrients, 2024. 16(21): p. 3586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16213586
Xiaoxiao, Y., et al., Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: A Review. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2021. 28(31): p. 6375-6394. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867328666210113170941
Verbunt, J. and F.R. Stassen, Probiotic membrane vesicles: emerging tools for disease treatment. Microbiome Research Reports, 2025. 4(2): p. N/A-N/A. https://doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2025.20
Adeoye, T., S.I. Shah, and G. Ullah, Systematic Analysis of Biological Processes Reveals Gene Co-expression Modules Driving Pathway Dysregulation in Alzheimer's Disease. bioRxiv, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.15.585267
Bordanaba-Florit, G., et al., Using single-vesicle technologies to unravel the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. Nature Protocols, 2021. 16(7): p. 3163-3185. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-021-00551-z
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ronghua Yuan, Fei Liu, Jingang Yu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









