Prediabetes and the risk of incident chronic kidney disease in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2026.13524Keywords:
Prediabetes, chronic kidney disease, risk factor, incidence, meta-analysisAbstract
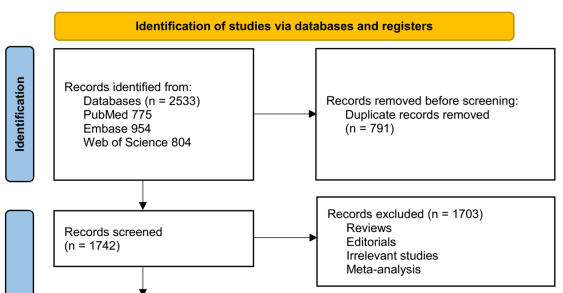
The relationship between prediabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains ambiguous, with varying results across cohort studies. This meta-analysis aimed to assess whether prediabetes is linked to an increased risk of developing incident CKD in the general adult population. A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science from inception to September 28, 2025, for longitudinal observational studies that evaluated CKD risk in individuals with prediabetes compared to those with normoglycemia. Prediabetes was defined by impaired fasting glucose (IFG), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), elevated glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), or a combination of these criteria. Pooled risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Fifteen cohorts comprising 2,854,724 participants were included in the analysis. The results indicated that prediabetes was significantly associated with an increased risk of incident CKD (RR: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.12–1.31; I² = 90%). Subgroup analyses revealed that the association was not significantly influenced by the definitions of prediabetes, study design, demographic characteristics of the population, follow-up duration, or study quality scores (p for subgroup difference all > 0.05). Meta-regression analysis suggested that a higher mean age of the population was inversely correlated with the observed effect size for the relationship between prediabetes and CKD risk (coefficient = -0.030, p = 0.004; adjusted R² = 67%). In conclusion, prediabetes is associated with a modestly elevated risk of developing CKD in the general population, with a potentially stronger correlation observed in younger individuals. These findings indicate an association rather than causality and suggest that early glycemic dysregulation may be linked to subsequent renal risk prior to the onset of overt diabetes.
Citations
Downloads
References
Francis A, Harhay MN, Ong ACM, Tummalapalli SL, Ortiz A, Fogo AB, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024;20(7):473–85.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6
Shao Y, Fan Y, Gao J, Meng H, Wang M, Shi Q, et al. Prevalence, awareness, and treatment of chronic kidney disease among adults in Yunnan Province, China: findings from the 2023 chronic disease and risk factors surveillance. Front Public Health. 2025;13:1685691.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1685691
Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Adamczak M, de Oliveira RB, Massy ZA, Sarafidis P, et al. Cardiovascular complications in chronic kidney disease: a review from the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group of the European Renal Association. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;119(11):2017–32.
https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvad083
Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, El Nahas M, Astor BC, Matsushita K, et al. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int. 2011;80(1):17–28.
https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.483
Gembillo G, Ingrasciotta Y, Crisafulli S, Luxi N, Siligato R, Santoro D, et al. Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: From Pathophysiology to Pharmacological Aspects with a Focus on Therapeutic Inertia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4824.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094824
Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Perreault L, Ji L, Dagogo-Jack S. Diagnosis and Management of Prediabetes: A Review. JAMA. 2023;329(14):1206–16.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.4063
Davidson MB. Historical review of the diagnosis of prediabetes/intermediate hyperglycemia: Case for the international criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;185:109219.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109219
Rico Fontalvo J, Soler MJ, Daza Arnedo R, Navarro-Blackaller G, Medina-González R, Rodríguez Yánez T, et al. Prediabetes and CKD: Does a causal relationship exist. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024;44(5):628–38.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nefroe.2024.11.005
Jadhakhan F, Marshall T, Gill P. A systematic review investigating the cumulative incidence of chronic kidney disease in young adults with impaired glucose tolerance. Syst Rev. 2015;4:69.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-015-0059-6
Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Narayan KM, Weisman D, Golden SH, Jaar BG. Association between prediabetes and risk of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2016;33(12):1615–24.
https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13113
Michishita R, Matsuda T, Kawakami S, Tanaka S, Kiyonaga A, Tanaka H, et al. Hypertension and hyperglycemia and the combination thereof enhances the incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in middle-aged and older males. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39(7):645–54.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2017.1306541
Jadhakhan F, Marshall T, Ryan R, Gill P. Risk of chronic kidney disease in young adults with impaired glucose tolerance/impaired fasting glucose: a retrospective cohort study using electronic primary care records. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19(1):42.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0834-4
Koshi T, Sagesaka H, Sato Y, Hirabayashi K, Koike H, Yamauchi K, et al. Elevated haemoglobin A1c but not fasting plasma glucose conveys risk of chronic kidney disease in non-diabetic individuals. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;146:233–9.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.10.026
Kim GS, Oh HH, Kim SH, Kim BO, Byun YS. Association between prediabetes (defined by HbA1(C), fasting plasma glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance) and the development of chronic kidney disease: a 9-year prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2019;20(1):130.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1307-0
Chen C, Liu G, Yu X, Yu Y. Association between Prediabetes and Renal Dysfunction from a Community-based Prospective Study. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(11):1515–21.
https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.46477
Furukawa M, Onoue T, Kato K, Wada T, Shinohara Y, Kinoshita F, et al. Prediabetes is associated with proteinuria development but not with glomerular filtration rate decline: A longitudinal observational study. Diabet Med. 2021;38(8):e14607.
https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14607
Honigberg MC, Zekavat SM, Pirruccello JP, Natarajan P, Vaduganathan M. Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes Across the Glycemic Spectrum: Insights From the UK Biobank. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;78(5):453–64.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2021.05.004
Manouchehri M, Cea-Soriano L, Franch-Nadal J, Ruiz A, Goday A, Villanueva R, et al. Heterogeneity in the association between prediabetes categories and reduction on glomerular filtration rate in a 5-year follow-up. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7373.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11392-5
Okawa Y, Suzuki E, Mitsuhashi T, Tsuda T, Yorifuji T. A population-based longitudinal study on glycated hemoglobin levels and new-onset chronic kidney disease among non-diabetic Japanese adults. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):13770.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40300-8
Zhang X, Wu H, Fan B, Shi M, Lau ESH, Yang A, et al. The role of age on the risk relationship between prediabetes and major morbidities and mortality: Analysis of the Hong Kong diabetes surveillance database of 2 million Chinese adults. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023;30:100599.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100599
Rooney MR, Wallace AS, Echouffo Tcheugui JB, Fang M, Hu J, Lutsey PL, et al. Prediabetes is associated with elevated risk of clinical outcomes even without progression to diabetes. Diabetologia. 2025;68(2):357–66.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-024-06315-0
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2021.
www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. 2010.
http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Zhang J, Yu KF. What's the relative risk? A method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes. JAMA. 1998;280(19):1690–1.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.280.19.1690
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Marušić MF, Fidahić M, Cepeha CM, Farcaș LG, Tseke A, Puljak L. Methodological tools and sensitivity analysis for assessing quality or risk of bias used in systematic reviews published in the high-impact anesthesiology journals. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2020;20(1):121.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-00966-4
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Fox CS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Meigs JB, Wilson PW, Levy D. Glycemic status and development of kidney disease: the Framingham Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(10):2436–40.
https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.10.2436
Schöttker B, Brenner H, Koenig W, Müller H, Rothenbacher D. Prognostic association of HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose with reduced kidney function in subjects with and without diabetes mellitus. Results from a population-based cohort study from Germany. Prev Med. 2013;57(5):596–600.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2013.08.002
Melsom T, Schei J, Stefansson VT, Solbu MD, Jenssen TG, Mathisen UD, et al. Prediabetes and Risk of Glomerular Hyperfiltration and Albuminuria in the General Nondiabetic Population: A Prospective Cohort Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;67(6):841–50.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.10.025
Tatsumi Y, Morimoto A, Soyano F, Shimoda T, Miyamatsu N, Ohno Y, et al. Risk of proteinuria among individuals with persistent borderline diabetes: the Saku study. Diabetol Int. 2016;7(2):181–7.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0235-x
Ping WX, Hu S, Su JQ, Ouyang SY. Metabolic disorders in prediabetes: From mechanisms to therapeutic management. World J Diabetes. 2024;15(3):361–77.
https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.361
Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, Bakris GL, Brosius FC, Kolkhof P, et al. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022;102(2):248–60.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.05.012
Kim JA, Montagnani M, Koh KK, Quon MJ. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms. Circulation. 2006;113(15):1888–904.
https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.563213
Giri B, Dey S, Das T, Sarkar M, Banerjee J, Dash SK. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:306–28.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.157
De Cosmo S, Menzaghi C, Prudente S, Trischitta V. Role of insulin resistance in kidney dysfunction: insights into the mechanism and epidemiological evidence. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(1):29–36.
https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfs290
Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ. Advanced glycation end products in the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018;93(4):803–13.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2017.11.034
Lovshin JA, Boulet G, Lytvyn Y, Lovblom LE, Bjornstad P, Farooqi MA, et al. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation in long-standing type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight. 2018;3(1):e96968.
https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.96968
Wei S, Fu Y, Zeng Y, Wu W, Cai J, Dong Z. Lipid metabolism in AKI and AKI-CKD transition: Dysregulation, lipotoxicity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 2025;275:108930.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108930
Ravender R, Roumelioti ME, Schmidt DW, Unruh ML, Argyropoulos C. Chronic Kidney Disease in the Older Adult Patient with Diabetes. J Clin Med. 2024;13(2):348.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020348
Gaillard F, Rabah MO, Aubert O, Garcelon N, Neuraz A, Legendre C, et al. Impact of Muscle Mass on the Performance of Creatinine-Based eGFR Equations and Mortality Risk Assessment After Kidney Transplantation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025;16(5):e70032.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.70032
Crews DC, Kuczmarski MF, Miller ER 3rd, Zonderman AB, Evans MK, Powe NR. Dietary habits, poverty, and chronic kidney disease in an urban population. J Ren Nutr. 2015;25(2):103–10.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2014.07.008
Baranowska-Jurkun A, Matuszewski W, Bandurska-Stankiewicz E. Chronic Microvascular Complications in Prediabetic States-An Overview. J Clin Med. 2020;9(10):3289.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103289
Tuso P. Prediabetes and lifestyle modification: time to prevent a preventable disease. Perm J. 2014;18(3):88–93.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Sitian Fang, Jinjing Huang, Yanxia Chen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









