Integrins and pulmonary fibrosis: Pathogenic roles and therapeutic opportunities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12545Keywords:
integrin, pulmonary fibrosis, PF, targeted therapyAbstract
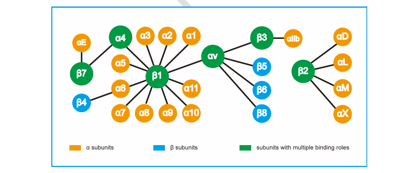
Characterized by the formation of fibrotic scars, pulmonary fibrosis (PF) involves a complex pathogenesis, limited treatment options, and a high mortality rate. Integrins—heterodimeric transmembrane proteins composed of α and β subunits—mediate extracellular matrix remodeling and regulate the physiological functions of epithelial, mesenchymal, and immune cells through "inside-out" and "outside-in" signaling pathways. These molecules play a critical role in the initiation and progression of PF. Due to their central regulatory functions, a range of integrin-targeted therapies has been developed. However, the complex pathophysiology of PF and the structural diversity of integrins pose significant challenges to targeted treatment. In this study, we systematically delineated the signaling networks mediated by the full spectrum of integrin family members and uncovered the molecular mechanisms by which they contribute to PF through immunoregulatory pathways. We also reviewed the development of integrin-based therapies from preclinical studies to clinical trials and discussed current priorities in clinical, basic, and translational research. These insights may provide new perspectives for the diagnosis and treatment of PF.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Zhangyang Bi, Guodong Zang, Xiaodong Wang, Li Tian, Wei Zhang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









