Comparison of the vitality tests used in the dental clinical practice and histological analysis of the dental pulp
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.6841Keywords:
Pulse oximetry, electrical sensibility test, histology, volume density of blood vessels and myelinated nerve fibersAbstract
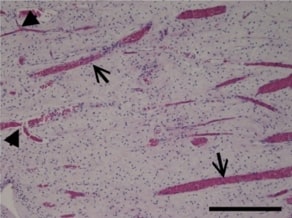
In dentistry, indirect diagnostic methods such as electrical sensibility testing and pulse oximetry are used to assess the status of the pulp. Our study aimed to determine the correlation between hemoglobin oxygen saturation and vascular volume density (Vvasc). We also wanted to examine an electrical sensibility test and the volume density of myelinated nerve fibers (Vnerv). Twenty-six intact permanent premolars were included in the study. For histological analysis, the pulp tissue was stained with hematoxylin-eosin and immunohistochemically for von Willebrand factor and S100 to detect blood vessels and myelinated nerve fibers, respectively. The stereological analysis was used to determine the Vvasc and Vnerv. Statistical analysis was done using the Pearson correlation test and Welch’s ANOVA test. Histological analysis showed that the pulp tissue was strongly vascularized and innervated. A significant positive correlation was found between Vvasc and hemoglobin oxygen saturation levels (p=0.030). A significant negative correlation was found between Vnerv and the lowest electrical voltage that patient felt (p=0.033). According to the maturity of the dental apex, teeth were divided into a group with open (N=6, OA group) and closed apex (N=20, CA group). We found that pulps in the CA group had higher Vnerv than the OA group (p=0.037). In contrast, there were no significant differences in Vvasc of the pulp tissue (p=0.059), oxygen saturation (p=0.907), or electrical voltage (p=0.113) between both groups. We can conclude that the measurement of pulse oximetry and electrical sensibility test reflect the morphology of healthy pulp tissue independently of the maturity of the dental apex.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Ana Tenyi, Lidija Nemeth, Aljaž Golež, Ksenija Cankar, Aleksandra Milutinović

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-01-02
Published 2022-06-01









